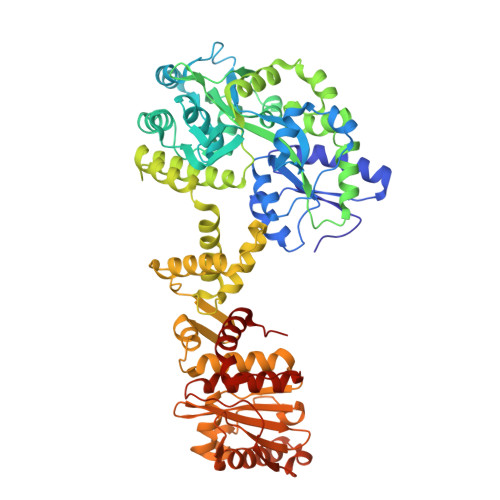
PELP1 coordinates the modular assembly and enzymatic activity of the rixosome complex.
Gordon, J., Kaminski, A.M., Bommu, S.R., Skrajna, A., Petrovich, R.M., Pedersen, L.C., McGinty, R.K., Warren, A.J., Stanley, R.E.(2025) Sci Adv 11: eadw4603-eadw4603
- PubMed: 40712028
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adw4603
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9ME8 - PubMed Abstract:
The rixosome is a large multisubunit complex that initiates RNA decay during critical nuclear transactions including ribosome assembly and heterochromatin maintenance. The overall architecture of the complex remains undefined because several subunits contain intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs). Here, we combined structural and functional approaches to establish PELP1 as the central scaffold of the rixosome upon which the enzymatic subunits modularly assemble. The C-terminal half of PELP1 is composed of a proline-rich IDR that mediates association with the AAA-ATPase MDN1, histones, and the SUMO-specific protease SENP3. The PELP1 IDR contains a glutamic acid-rich region that we establish can chaperone the histone octamer in vitro. Last, the x-ray structure of a small linear motif (SLiM) from the PELP IDR bound to SENP3 reveals how PELP1 allosterically activates SUMO protease activity. This work provides an integrated structural model for understanding the rixosome's dynamic architecture and how it modularly coordinates several cellular functions.
- Molecular and Cellular Biology Laboratory, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: