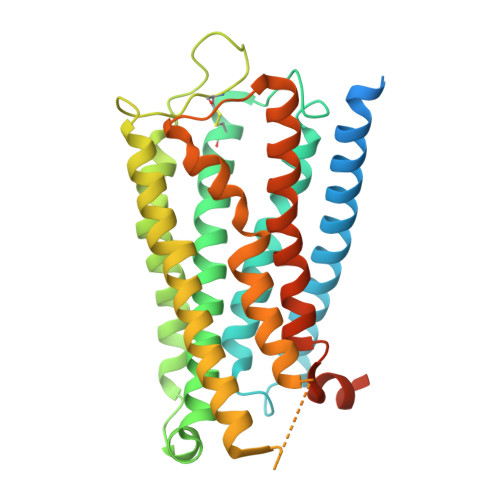
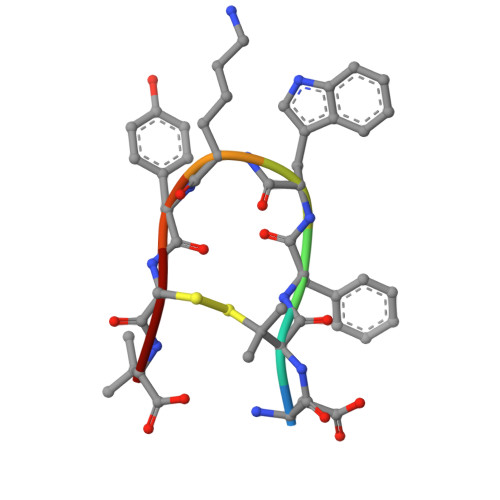
Structural insights into hormone recognition and G-protein coupling of the urotensin-II receptor.
Gao, T., You, C., Cao, Y., Xu, X., Yuan, Q., Shen, S., Xu, H.E., Duan, J.(2025) J Biological Chem 301: 110794-110794
- PubMed: 41062066
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110794
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9JFK - PubMed Abstract:
Urotensin-II (U-II) is a potent vasoconstrictor peptide that interacts with the human urotensin-II receptor (UTR), a class A G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that primarily couples with G q proteins. In this study, we present the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the miniG q -coupled UTR bound to the potent UTR agonist P5U, providing insights into unique ligand recognition and activation mechanisms. Unlike typical linear peptides, the cyclic structure of P5U engages the receptor's transmembrane domains through key side chain interactions involving residues F6, W7, K8, and Y9, which are crucial for receptor activation. Comparative analysis with somatostatin receptors (SSTRs) reveals distinct ligand specificity, driven by variations in side chain composition. Notably, we identify F274 6.51 as the toggle switch residue in UTR, in contrast to the classical W 6.48 seen in other GPCRs. Our findings elucidate the structural basis for UTR's G q coupling specificity, highlighting unique Gα q interactions. This study advances the understanding of U-II signaling and offers a foundation for developing selective UTR modulators, with potential therapeutic implications for cardiovascular diseases linked to dysregulated U-II activity.
- School of Life Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, China; State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: