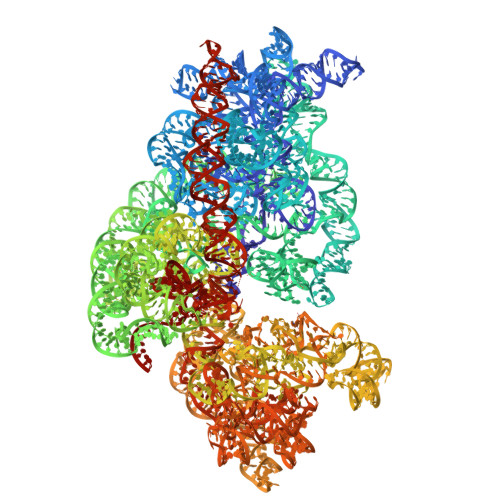
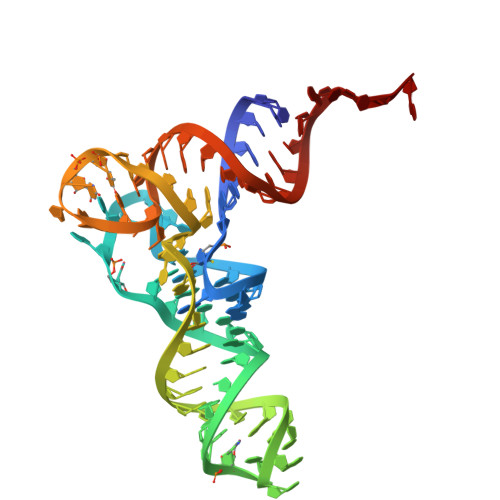
Molecular basis of mRNA delivery to the bacterial ribosome.
Webster, M.W., Chauvier, A., Rahil, H., Graziadei, A., Charles, K., Miropolskaya, N., Takacs, M., Saint-Andre, C., Rappsilber, J., Walter, N.G., Weixlbaumer, A.(2024) Science 386: eado8476-eado8476
- PubMed: 39607923
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.ado8476
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9GR1, 9GUP, 9GUQ, 9GUR, 9GUS, 9GUT, 9GUU, 9GUV, 9GUW, 9GUX - PubMed Abstract:
Protein synthesis begins with the formation of a ribosome-messenger RNA (mRNA) complex. In bacteria, the small ribosomal subunit (30 S ) is recruited to many mRNAs through base pairing with the Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence and RNA binding by ribosomal protein bS1. Translation can initiate on nascent mRNAs, and RNA polymerase (RNAP) can promote the recruitment of the pioneering 30 S . Here, we examined 30 S recruitment to nascent mRNAs using cryo-electron microscopy, single-molecule fluorescence colocalization, and in-cell cross-linking mass spectrometry. We show that bS1 delivers the mRNA to the ribosome for SD duplex formation and 30 S activation. Additionally, bS1 and RNAP stimulate translation initiation. Our work provides a mechanistic framework for how the SD duplex, ribosomal proteins, and RNAP cooperate in 30 S recruitment to mRNAs and establish transcription-translation coupling.
- Department of Integrated Structural Biology, Institut de Génétique et de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire (IGBMC), Illkirch Cedex, France.
Organizational Affiliation: