Depsides from Origanum dictamnus and Satureja pilosa as selective inhibitors of carbonic anhydrases: Isolation, structure elucidation, X-ray crystallography.
Paloukopoulou, C., Ntagli, O.S., Gherardi, L., Dourdouni, V., Filippou, G., Alterio, V., Giovannuzzi, S., Massardi, M.L., De Simone, G., Ronca, R., Supuran, C.T., Pescitelli, G., Karioti, A.(2025) Arch Pharm (Weinheim) 358: e2400823-e2400823
- PubMed: 39711099
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ardp.202400823
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9G38 - PubMed Abstract:
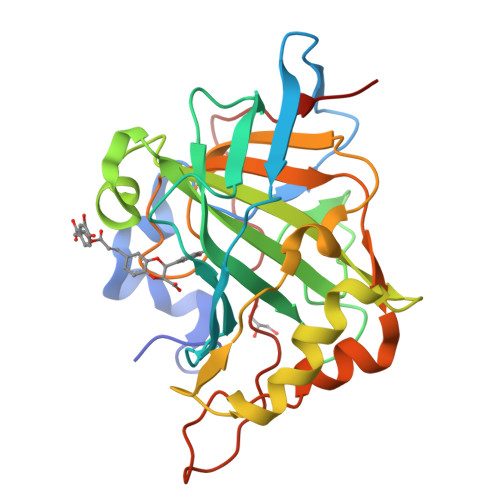
In this study, four depsides were isolated from Origanum dictamnus L. and Satureja pilosa Velen. medicinal plants and their structures were assessed by means of one-dimensional (1D)- and two-dimensional (2D)-nuclear magnetic resonance, high resolution mass spectrometry, and electronic circular dichroism analyses. The compound 1, herein reported for the first time, salvianolic acid P 2, clinopodic acid I 3, and clinopodic acid O 4 were all profiled in vitro on a panel of human (h) expressed carbonic anhydrases (CAs; EC 4.2.1.1) and preferential inhibition for the tumor-associated human carbonic anhydrase (hCA) IX and hCA XII over the constitutively expressed hCA I and hCA II isoforms was observed. X-ray crystallography allowed us to assess the binding mode of salvianolic acid P 2 to hCA II. The compounds exhibited significant cytotoxic effects on the human triple-negative breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231, suggesting that this class of depsides are promising molecules for future investigation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Pharmacognosy, Department of Pharmacy, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece.