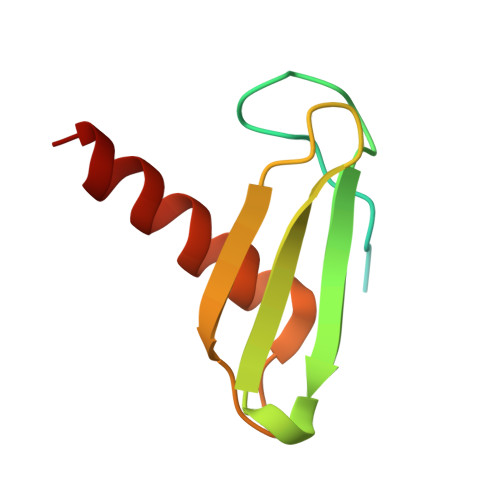
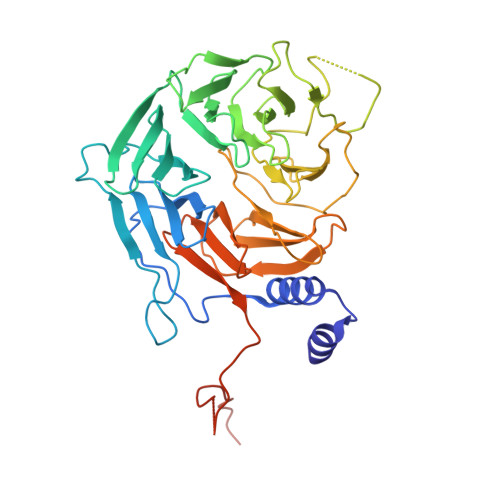
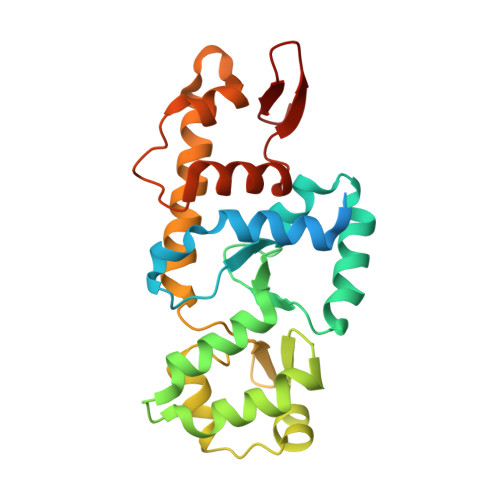
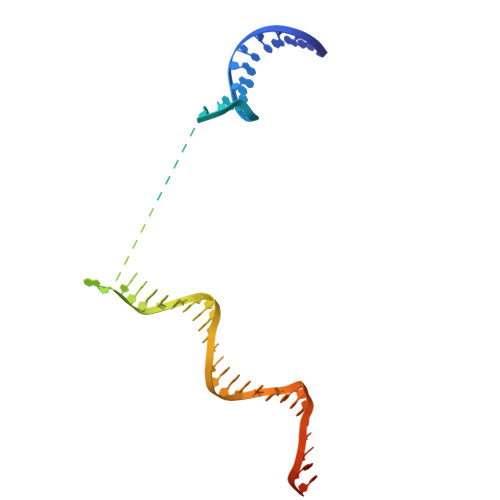
STK19 drives transcription-coupled repair by stimulating repair complex stability, RNA Pol II ubiquitylation, and TFIIH recruitment.
Ramadhin, A.R., Lee, S.H., Zhou, D., Salmazo, A., Gonzalo-Hansen, C., van Sluis, M., Blom, C.M.A., Janssens, R.C., Raams, A., Dekkers, D., Bezstarosti, K., Slade, D., Vermeulen, W., Pines, A., Demmers, J.A.A., Bernecky, C., Sixma, T.K., Marteijn, J.A.(2024) Mol Cell 84: 4740
- PubMed: 39547223
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2024.10.030
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9FD2 - PubMed Abstract:
Transcription-coupled nucleotide excision repair (TC-NER) efficiently eliminates DNA damage that impedes gene transcription by RNA polymerase II (RNA Pol II). TC-NER is initiated by the recognition of lesion-stalled RNA Pol II by CSB, which recruits the CRL4 CSA ubiquitin ligase and UVSSA. RNA Pol II ubiquitylation at RPB1-K1268 by CRL4 CSA serves as a critical TC-NER checkpoint, governing RNA Pol II stability and initiating DNA damage excision by TFIIH recruitment. However, the precise regulatory mechanisms of CRL4 CSA activity and TFIIH recruitment remain elusive. Here, we reveal human serine/threonine-protein kinase 19 (STK19) as a TC-NER factor, which is essential for correct DNA damage removal and subsequent transcription restart. Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) studies demonstrate that STK19 is an integral part of the RNA Pol II-TC-NER complex, bridging CSA, UVSSA, RNA Pol II, and downstream DNA. STK19 stimulates TC-NER complex stability and CRL4 CSA activity, resulting in efficient RNA Pol II ubiquitylation and correct UVSSA and TFIIH binding. These findings underscore the crucial role of STK19 as a core TC-NER component.
- Department of Molecular Genetics, Oncode Institute, Erasmus MC Cancer Institute, Erasmus University Medical Center, 3015 CN Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
Organizational Affiliation: