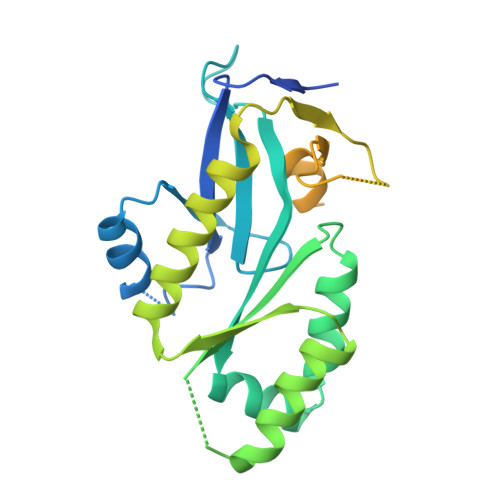
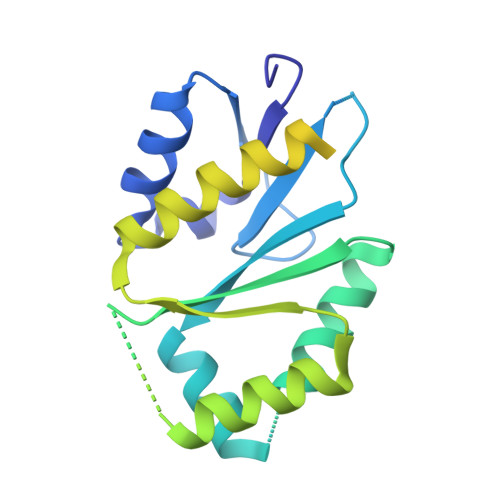
Fragment-Based Discovery of Novel MUS81 Inhibitors.
Collie, G.W., Borjesson, U., Chen, Y., Dong, Z., Di Fruscia, P., Gohlke, A., Hoyle, A., Hunt, T.A., Jesani, M.H., Luo, H., Luptak, J., Milbradt, A.G., Narasimhan, P., Packer, M., Patel, S., Qiao, J., Storer, R.I., Stubbs, C.J., Tart, J., Truman, C., Wang, A.T., Wheeler, M.G., Winter-Holt, J.(2024) ACS Med Chem Lett 15: 1151-1158
- PubMed: 39015284
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.3c00453
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9F98, 9F99, 9F9A, 9F9K, 9F9L, 9F9M - PubMed Abstract:
MUS81 is a structure-selective endonuclease that cleaves various branched DNA structures arising from natural physiological processes such as homologous recombination and mitosis. Due to this, MUS81 is able to relieve replication stress, and its function has been reported to be critical to the survival of many cancers, particularly those with dysfunctional DNA-repair machinery. There is therefore interest in MUS81 as a cancer drug target, yet there are currently few small molecule inhibitors of this enzyme reported, and no liganded crystal structures are available to guide hit optimization. Here we report the fragment-based discovery of novel small molecule MUS81 inhibitors with sub-μM biochemical activity. These inhibitors were used to develop a novel crystal system, providing the first structural insight into the inhibition of MUS81 with small molecules.
- R&D, AstraZeneca, Cambridge CB2 0AA, U.K.
Organizational Affiliation: