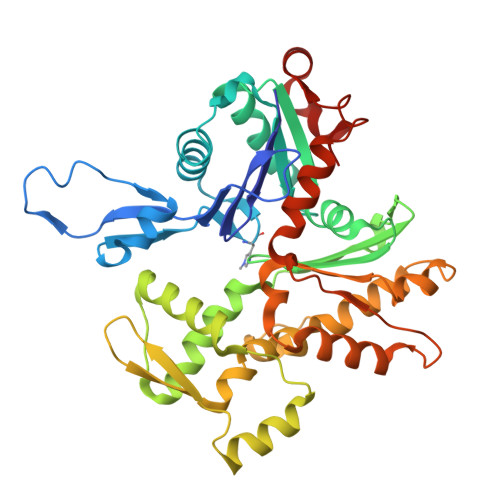
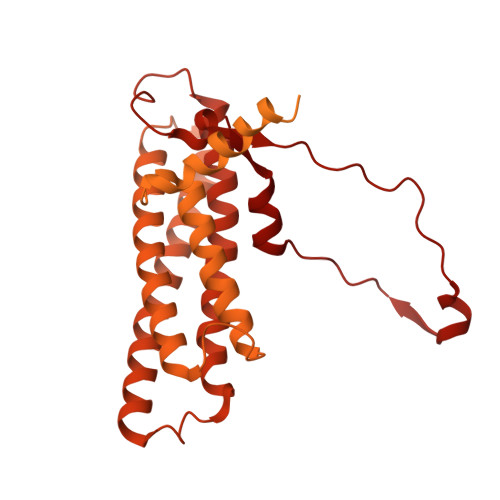
Afadin mediates cadherin-catenin complex clustering on F-actin linked to cooperative binding and filament curvature.
Gong, R., Reynolds, M.J., Sun, X., Alushin, G.M.(2024) bioRxiv
- PubMed: 39415991
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.10.08.617332
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9DVA - PubMed Abstract:
The E-cadherin-β-catenin-αE-catenin (cadherin-catenin) complex couples the cytoskeletons of neighboring cells at adherens junctions (AJs) to mediate force transmission across epithelia. Mechanical force and auxiliary binding partners converge to stabilize the cadherin-catenin complex's inherently weak binding to actin filaments (F-actin) through unclear mechanisms. Here we show that afadin's coiled-coil (CC) domain and vinculin synergistically enhance the cadherin-catenin complex's F-actin engagement. The cryo-EM structure of an E-cadherin-β-catenin-αE-catenin-vinculin-afadin-CC supra-complex bound to F-actin reveals that afadin-CC bridges adjacent αE-catenin actin-binding domains along the filament, stabilizing flexible αE-catenin segments implicated in mechanical regulation. These cooperative binding contacts promote the formation of supra-complex clusters along F-actin. Additionally, cryo-EM variability analysis links supra-complex binding along individual F-actin strands to nanoscale filament curvature, a deformation mode associated with cytoskeletal forces. Collectively, this work elucidates a mechanistic framework by which vinculin and afadin tune cadherin-catenin complex-cytoskeleton coupling to support AJ function across varying mechanical regimes.
- Laboratory of Structural Biophysics and Mechanobiology, The Rockefeller University, New York, NY, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: