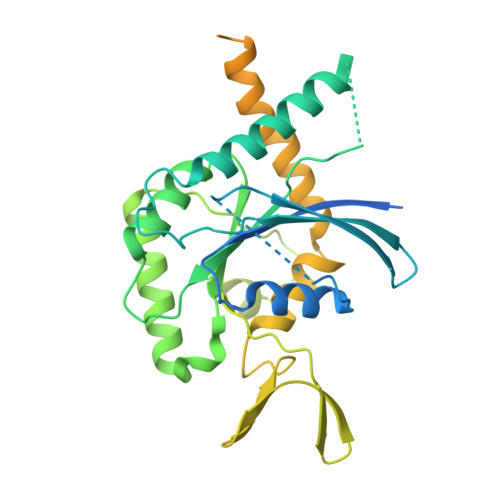
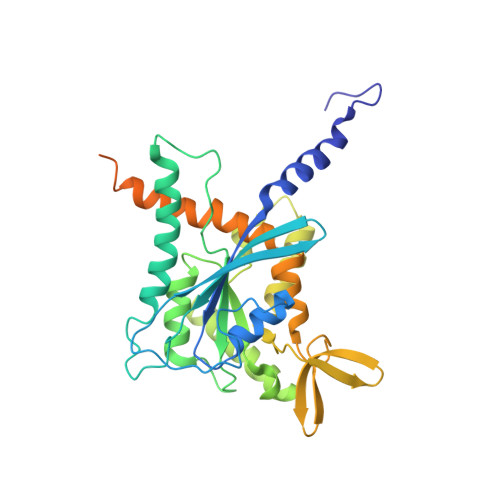
Structural Insights into Ciona intestinalis Septins: Complexes Suggest a Mechanism for Nucleotide-dependent Interfacial Cross-talk.
Mendonca, D.C., Morais, S.T.B., Ciol, H., Pinto, A.P.A., Leonardo, D.A., Pereira, H.D., Valadares, N.F., Portugal, R.V., Klaholz, B.P., Garratt, R.C., Araujo, A.P.U.(2024) J Mol Biology 436: 168693-168693
- PubMed: 38960133
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168693
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9BHT, 9BHW - PubMed Abstract:
Septins are filamentous nucleotide-binding proteins which can associate with membranes in a curvature-dependent manner leading to structural remodelling and barrier formation. Ciona intestinalis, a model for exploring the development and evolution of the chordate lineage, has only four septin-coding genes within its genome. These represent orthologues of the four classical mammalian subgroups, making it a minimalist non-redundant model for studying the modular assembly of septins into linear oligomers and thereby filamentous polymers. Here, we show that C. intestinalis septins present a similar biochemistry to their human orthologues and also provide the cryo-EM structures of an octamer, a hexamer and a tetrameric sub-complex. The octamer, which has the canonical arrangement (2-6-7-9-9-7-6-2) clearly shows an exposed NC-interface at its termini enabling copolymerization with hexamers into mixed filaments. Indeed, only combinations of septins which had CiSEPT2 occupying the terminal position were able to assemble into filaments via NC-interface association. The CiSEPT7-CiSEPT9 tetramer is the smallest septin particle to be solved by Cryo-EM to date and its good resolution (2.7 Å) provides a well-defined view of the central NC-interface. On the other hand, the CiSEPT7-CiSEPT9 G-interface shows signs of fragility permitting toggling between hexamers and octamers, similar to that seen in human septins but not in yeast. The new structures provide insights concerning the molecular mechanism for cross-talk between adjacent interfaces. This indicates that C. intestinalis may represent a valuable tool for future studies, fulfilling the requirements of a complete but simpler system to understand the mechanisms behind the assembly and dynamics of septin filaments.
- São Carlos Institute of Physics, USP, São Carlos, SP, Brazil.
Organizational Affiliation: