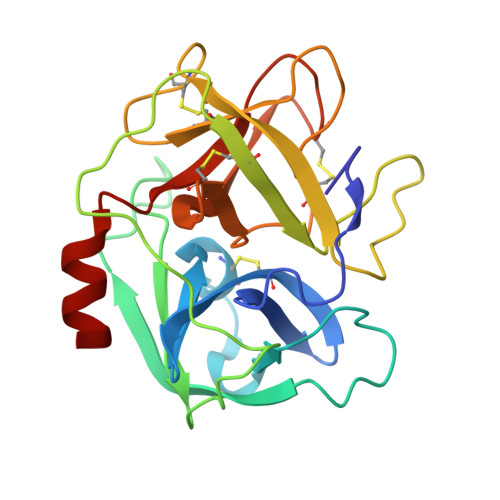
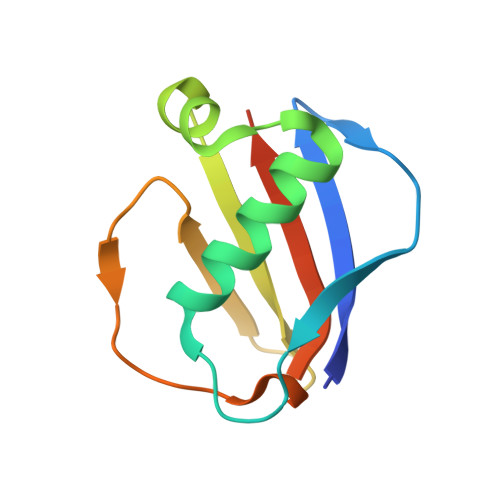
S. aureus Eap is a polyvalent inhibitor of neutrophil serine proteases.
Mishra, N., Gido, C.D., Herdendorf, T.J., Hammel, M., Hura, G.L., Fu, Z.Q., Geisbrecht, B.V.(2024) J Biological Chem 300: 107627-107627
- PubMed: 39098536
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107627
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8D7I, 8D7K, 9ASS, 9ASX, 9ATK, 9ATU - PubMed Abstract:
Staphylococcus aureus expresses three high-affinity neutrophil serine protease (NSP) inhibitors known as the extracellular adherence protein domain (EAPs) proteins. Whereas EapH1 and EapH2 are comprised of a single EAP domain, the modular extracellular adherence protein (Eap) from S. aureus strain Mu50 consists of four EAP domains. We recently reported that EapH2 can simultaneously bind and inhibit cathepsin-G (CG) and neutrophil elastase (NE), which are the two most abundant NSPs. This unusual property of EapH2 arises from independent CG and NE-binding sites that lie on opposing faces of its EAP domain. Here we used X-ray crystallography and enzyme assays to show that all four individual domains of Eap (i.e. Eap1, Eap2, Eap3, and Eap4) exhibit an EapH2-like ability to form ternary complexes with CG and NE that inhibit both enzymes simultaneously. We found that Eap1, Eap2, and Eap3 have similar functional profiles insofar as NSP inhibition is concerned but that Eap4 displays an unexpected ability to inhibit two NE enzymes simultaneously. Using X-ray crystallography, we determined that this second NE-binding site in Eap4 arises through the same region of its EAP domain that also comprises its CG-binding site. Interestingly, small angle X-ray scattering data showed that stable tail-to-tail dimers of the NE/Eap4/NE ternary complex exist in solution. This arrangement is compatible with NSP-binding at all available sites in a two-domain fragment of Eap. Together, our work implies that Eap is a polyvalent inhibitor of NSPs. It also raises the possibility that higher-order structures of NSP-bound Eap may have unique functional properties.
- Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biophysics, Kansas State University, Manhattan, Kansas, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: