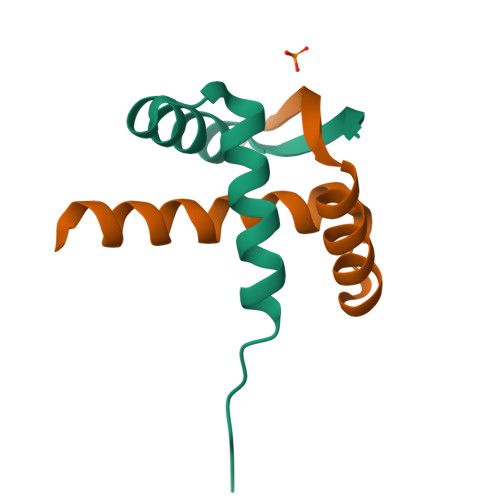
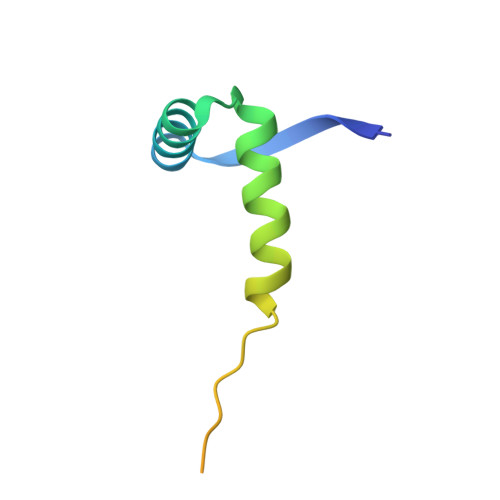
DNA binding reveals hidden interdomain allostery of a MazE antitoxin from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Eun, H.J., Lee, S.Y., Lee, K.Y.(2024) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 710: 149898-149898
- PubMed: 38598903
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.149898
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8YPJ - PubMed Abstract:
Type II toxin-antitoxin (TA) systems are ubiquitously distributed genetic elements in prokaryotes and are crucial for cell maintenance and survival under environmental stresses. The antitoxin is a modular protein consisting of the disordered C-terminal region that physically contacts and neutralizes the cognate toxin and the well-folded N-terminal DNA binding domain responsible for autorepression of TA transcription. However, how the two functional domains communicate is largely unknown. Herein, we determined the crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of the type II antitoxin MazE-mt10 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, revealing a homodimer of the ribbon-helix-helix (RHH) fold with distinct DNA binding specificity. NMR studies demonstrated that full-length MazE-mt10 forms the helical and coiled states in equilibrium within the C-terminal region, and that helical propensity is allosterically enhanced by the N-terminal binding to the cognate operator DNA. This coil-to-helix transition may promote toxin binding/neutralization of MazE-mt10 and further stabilize the TA-DNA transcription repressor. This is supported by many crystal structures of type II TA complexes in which antitoxins form an α-helical structure at the TA interface. The hidden helical state of free MazE-mt10 in solution, favored by DNA binding, adds a new dimension to the regulatory mechanism of type II TA systems. Furthermore, complementary approaches using X-ray crystallography and NMR allow us to study the allosteric interdomain interplay of many other full-length antitoxins of type II TA systems.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Research Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, Seoul National University, Seoul, 08826, Republic of Korea.