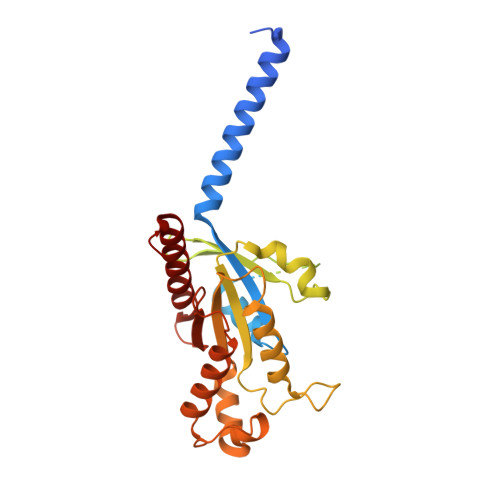
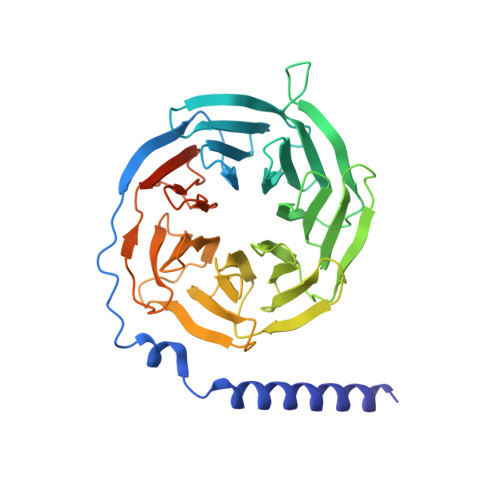
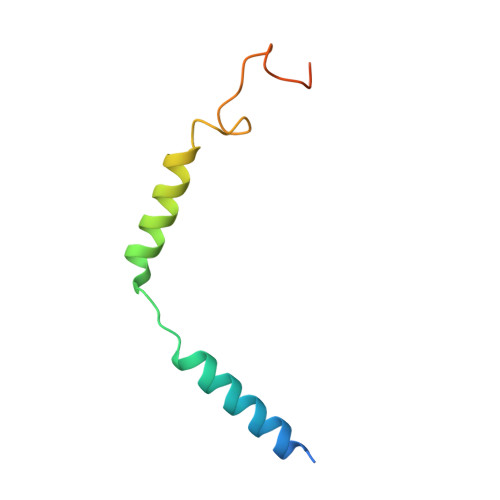
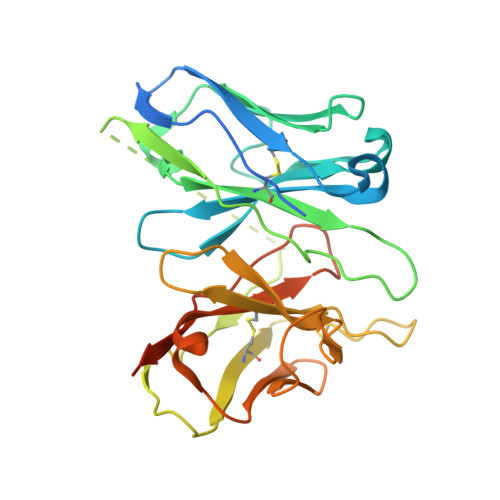
Bitter taste TAS2R14 activation by intracellular tastants and cholesterol.
Hu, X., Ao, W., Gao, M., Wu, L., Pei, Y., Liu, S., Wu, Y., Zhao, F., Sun, Q., Liu, J., Jiang, L., Wang, X., Li, Y., Tan, Q., Cheng, J., Yang, F., Yang, C., Sun, J., Hua, T., Liu, Z.J.(2024) Nature 631: 459-466
- PubMed: 38776963
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07569-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8XQL, 8XQN, 8XQO, 8XQP, 8XQR, 8XQS, 8XQT, 8YKY - PubMed Abstract:
Bitter taste receptors, particularly TAS2R14, play central roles in discerning a wide array of bitter substances, ranging from dietary components to pharmaceutical agents 1,2 . TAS2R14 is also widely expressed in extragustatory tissues, suggesting its extra roles in diverse physiological processes and potential therapeutic applications 3 . Here we present cryogenic electron microscopy structures of TAS2R14 in complex with aristolochic acid, flufenamic acid and compound 28.1, coupling with different G-protein subtypes. Uniquely, a cholesterol molecule is observed occupying what is typically an orthosteric site in class A G-protein-coupled receptors. The three potent agonists bind, individually, to the intracellular pockets, suggesting a distinct activation mechanism for this receptor. Comprehensive structural analysis, combined with mutagenesis and molecular dynamic simulation studies, elucidate the broad-spectrum ligand recognition and activation of the receptor by means of intricate multiple ligand-binding sites. Our study also uncovers the specific coupling modes of TAS2R14 with gustducin and G i1 proteins. These findings should be instrumental in advancing knowledge of bitter taste perception and its broader implications in sensory biology and drug discovery.
- iHuman Institute, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: