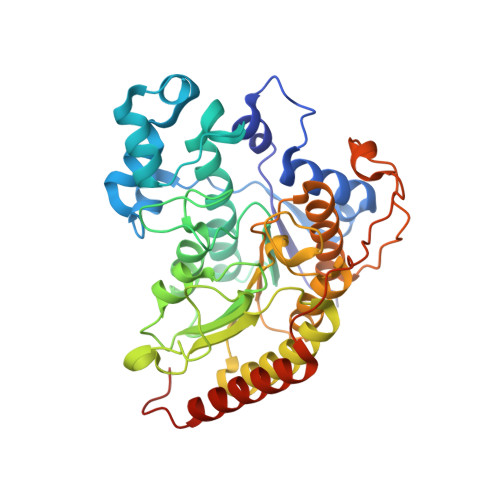
Structure-function analyses reveal Arabidopsis thaliana HDA7 to be an inactive histone deacetylase.
Saharan, K., Baral, S., Shaikh, N.H., Vasudevan, D.(2024) Curr Res Struct Biol 7: 100136-100136
- PubMed: 38463934
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crstbi.2024.100136
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8WZL - PubMed Abstract:
Histone deacetylases (HDACs), responsible for the removal of acetyl groups from histone tails, are important epigenetic factors. They play a critical role in the regulation of gene expression and are significant in the context of plant growth and development. The Rpd3/Hda1 family of HDACs is reported to regulate key biological processes in plants, such as stress response, seed, embryonic, and floral development. Here, we characterized Arabidopsis thaliana HDA7, a Class I, Rpd3/Hda1 family HDAC. SAXS and AUC results show that the recombinantly expressed and purified histone deacetylase domain of AtHDA7 exists as a monomer in solution. Further, the crystal structure showed AtHDA7 to fold into the typical α/β arginase fold, characteristic of Rpd3/Hda1 family HDACs. Sequence analysis revealed that the Asp and His residues of the catalytic 'XDXH' motif present in functional Rpd3/Hda1 family HDACs are mutated to Gly and Pro, respectively, in AtHDA7, suggesting that it might be catalytically inactive. The Asp and His residues are important for Zn 2+ -binding. Not surprisingly, the crystal structure did not have Zn 2+ bound in the catalytic pocket, which is essential for the HDAC activity. Further, our in vitro activity assay revealed AtHDA7 to be inactive as an HDAC. A search in the sequence databases suggested that homologs of AtHDA7 are found exclusively in the Brassicaceae family to which Arabidopsis belongs. It is possible that HDA7 descended from HDA6 through whole genome duplication and triplication events during evolution, as suggested in a previous phylogenetic study.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Laboratory, Institute of Life Sciences (ILS), Bhubaneswar, 751023, India.