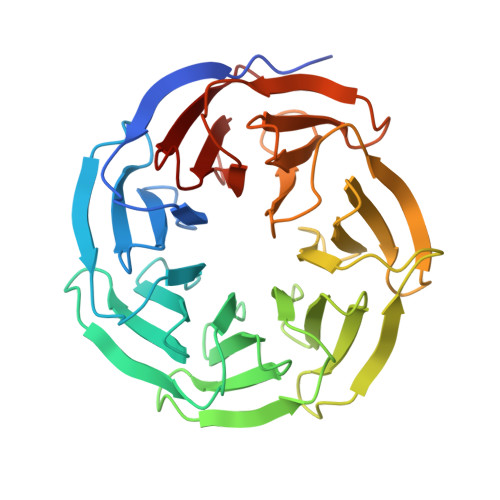
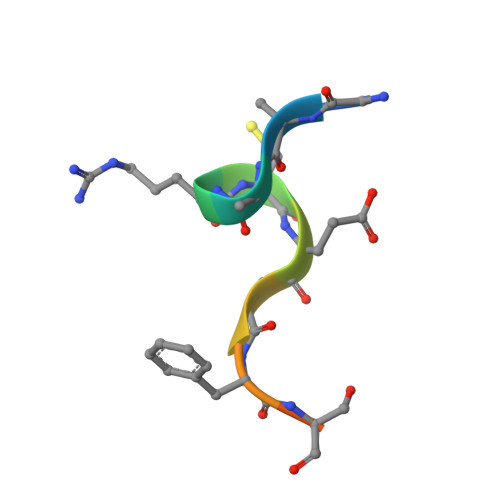
Structural studies of WDR5 in complex with MBD3C WIN motif reveal a unique binding mode.
Yang, Y., Xu, L., Zhang, S., Yao, L., Ding, Y., Li, W., Chen, X.(2024) J Biological Chem 300: 107468-107468
- PubMed: 38876301
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107468
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8WXQ, 8WXR, 8WXT, 8WXU, 8WXV, 8WXX - PubMed Abstract:
The nucleosome remodeling and deacetylase (NuRD) complex plays a pivotal role in chromatin regulation and transcriptional repression. In mice, methyl-CpG binding domain 3 isoform C (MBD3C) interacts specifically with the histone H3 binding protein WD repeat-containing protein 5 (WDR5) and forms the WDR5-MBD3C/NuRD complex. Despite the functional significance of this interaction on embryonic stem cells gene regulation, the molecular mechanism underlying MBD3C recognition by WDR5 remains elusive. Here, we determined the crystal structure of WDR5 in complex with the peptide (residues 40-51) derived from the MBD3C protein at a resolution of 1.9 Å. Structural analysis revealed that MBD3C utilizes a unique binding mode to interact with WDR5, wherein MBD3C Arg43 and Phe47 are involved in recognizing the WDR5-interacting (WIN) site and Tyr191-related B site on the small surface of WDR5, respectively. Notably, the binding induces a ∼91° rotation of WDR5 Tyr191, generating the hydrophobic B site. Furthermore, mutation experiments combined with isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) assays confirmed the importance of both Arg43 and Phe47 in mediating WDR5 binding affinity. By determining structures of various peptides bound to WDR5, we demonstrated that the WDR5 WIN site and B site can be concurrently recognized by WIN motif peptides containing ''Arg-Cys/Ser-Arg-Val-Phe'' consensus sequence. Overall, this study reveals the structural basis for the formation of the WDR5-MBD3C subcomplex and provides new insights into the recognition mode of WDR5 for the WIN motif. Moreover, these findings shed light on structural-based designs of WDR5-targeted anti-cancer small molecule inhibitors or peptide-mimic drugs.
- School of Life Sciences, Anhui University, Hefei, Anhui, 230601, China. Electronic address: ahuyy@ahu.edu.cn.
Organizational Affiliation: