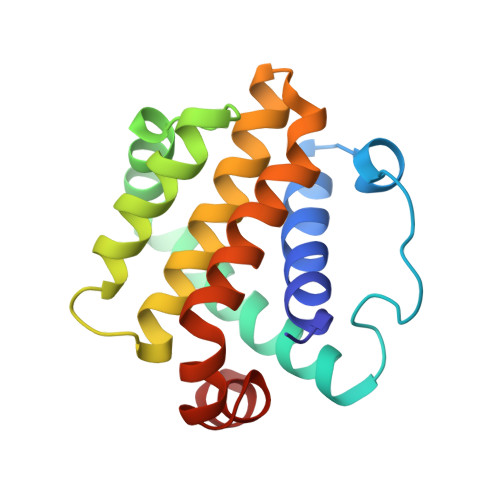
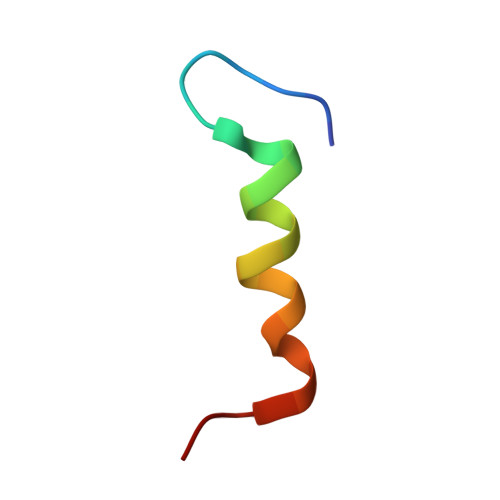
Structural Insights into the Interaction between the C-Terminal-Deleted BH3-like Motif Peptide of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein and Bcl-x L.
Kusunoki, H., Sakamoto, T., Kobayashi, N., Kohno, T., Wakamatsu, K., Nagata, T.(2024) Biochemistry 63: 632-643
- PubMed: 38377677
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.3c00709
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8WLS - PubMed Abstract:
Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) plays a crucial role in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) associated with hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. The full-length HBx protein interacts with Bcl-x L and is involved in the HBV replication and cell death processes. The three hydrophobic residues Trp120, Leu123, and Ile127 of the HBx BH3-like motif are essential for the Bcl-x L -binding. On the other hand, various lengths of C-terminal-truncated HBx mutants are frequently detected in HCC tissues, and these mutants, rather than the full-length HBx, appear to be responsible for HCC development. Notably, the region spanning residues 1-120 of HBx [HBx(1 and 120)] has been strongly associated with an increased risk of HCC development. However, the mode of interaction between HBx(1-120) and Bcl-x L remains unclear. HBx(1-120) possesses only Trp120 among the three hydrophobic residues essential for the Bcl-x L -binding. To elucidate this interaction mode, we employed a C-terminal-deleted HBx BH3-like motif peptide composed of residues 101-120. Here, we present the NMR complex structure of Bcl-x L and HBx(101-120). Our results demonstrate that HBx(101-120) binds to Bcl-x L in a weaker manner. Considering the high expression of Bcl-x L in HCC cells, this weak interaction, in conjunction with the overexpression of Bcl-x L in HCC cells, may potentially contribute to HCC development through the interaction between C-terminal-truncated HBx and Bcl-x L .
- Research Center for Biological Products in the Next Generation, National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Musashimurayama, Tokyo 208-0011, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: