Development of Benziodarone Analogues with Enhanced Potency for Selective Binding to Transthyretin in Human Plasma.
Mizuguchi, M., Nakagawa, Y., Yokoyama, T., Okada, T., Fujii, K., Takahashi, K., Luan, N.N.T., Nabeshima, Y., Kanamitsu, K., Nakagawa, S., Yamakawa, S., Ueda, M., Ando, Y., Toyooka, N.(2024) J Med Chem 67: 6987-7005
- PubMed: 38670538
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c02286
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8WGS, 8WGT, 8WGU - PubMed Abstract:
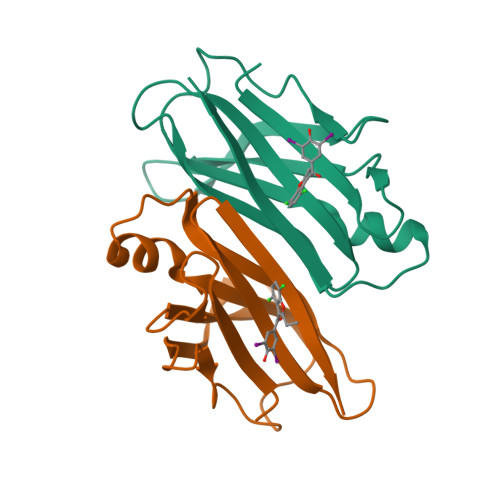
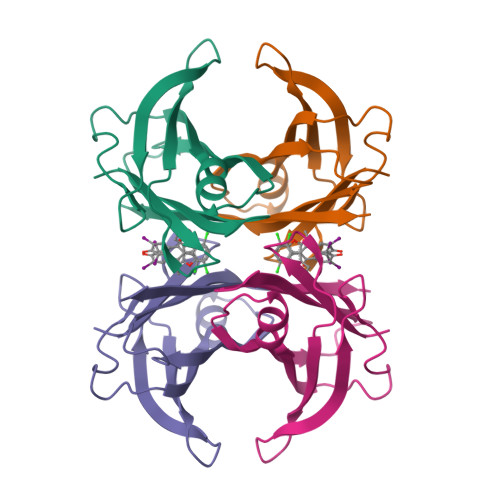
Transthyretin amyloidosis is a fatal disorder caused by transthyretin amyloid aggregation. Stabilizing the native structure of transthyretin is an effective approach to inhibit amyloid aggregation. To develop kinetic stabilizers of transthyretin, it is crucial to explore compounds that selectively bind to transthyretin in plasma. Our recent findings demonstrated that the uricosuric agent benziodarone selectively binds to transthyretin in plasma. Here, we report the development of benziodarone analogues with enhanced potency for selective binding to transthyretin in plasma compared to benziodarone. These analogues featured substituents of chlorine, bromine, iodine, a methyl group, or a trifluoromethyl group, at the 4-position of the benzofuran ring. X-ray crystal structure analysis revealed that CH···O hydrogen bonds and a halogen bond are important for the binding of the compounds to the thyroxine-binding sites. The bioavailability of benziodarone analogues with 4-Br, 4-Cl, or 4-CH 3 was comparable to that of tafamidis, a current therapeutic agent for transthyretin amyloidosis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Toyama, Toyama 930-0194, Japan.