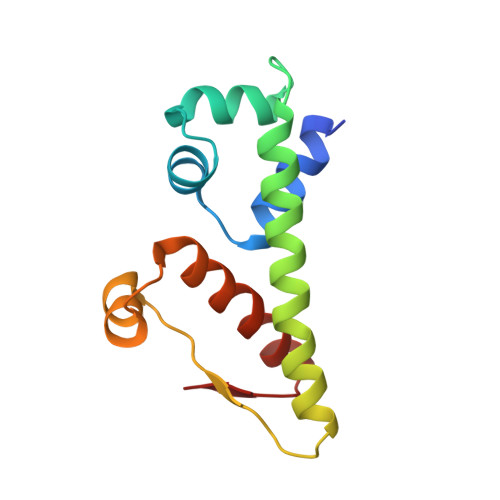
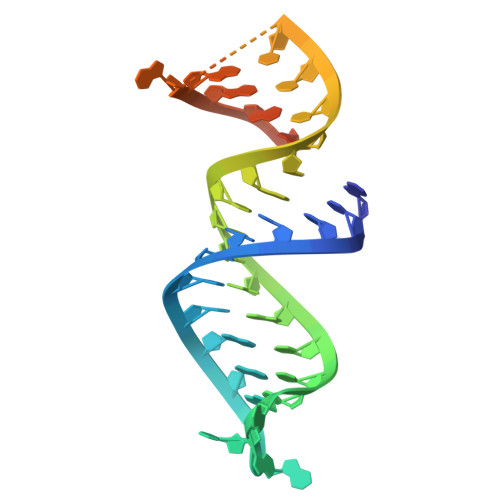
Phage anti-CRISPR control by an RNA- and DNA-binding helix-turn-helix protein.
Birkholz, N., Kamata, K., Feussner, M., Wilkinson, M.E., Cuba Samaniego, C., Migur, A., Kimanius, D., Ceelen, M., Went, S.C., Usher, B., Blower, T.R., Brown, C.M., Beisel, C.L., Weinberg, Z., Fagerlund, R.D., Jackson, S.A., Fineran, P.C.(2024) Nature 631: 670-677
- PubMed: 38987591
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07644-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8W35 - PubMed Abstract:
In all organisms, regulation of gene expression must be adjusted to meet cellular requirements and frequently involves helix-turn-helix (HTH) domain proteins 1 . For instance, in the arms race between bacteria and bacteriophages, rapid expression of phage anti-CRISPR (acr) genes upon infection enables evasion from CRISPR-Cas defence; transcription is then repressed by an HTH-domain-containing anti-CRISPR-associated (Aca) protein, probably to reduce fitness costs from excessive expression 2-5 . However, how a single HTH regulator adjusts anti-CRISPR production to cope with increasing phage genome copies and accumulating acr mRNA is unknown. Here we show that the HTH domain of the regulator Aca2, in addition to repressing Acr synthesis transcriptionally through DNA binding, inhibits translation of mRNAs by binding conserved RNA stem-loops and blocking ribosome access. The cryo-electron microscopy structure of the approximately 40 kDa Aca2-RNA complex demonstrates how the versatile HTH domain specifically discriminates RNA from DNA binding sites. These combined regulatory modes are widespread in the Aca2 family and facilitate CRISPR-Cas inhibition in the face of rapid phage DNA replication without toxic acr overexpression. Given the ubiquity of HTH-domain-containing proteins, it is anticipated that many more of them elicit regulatory control by dual DNA and RNA binding.
- Department of Microbiology and Immunology, University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand.
Organizational Affiliation: