Disulfi de constrained Fabs overcome target size limitation for high-resolution single-particle cryo-EM.
Kung, J.E., Johnson, M.C., Jao, C.C., Arthur, C.P., Tegunov, D., Rohou, A., Sudhamsu, J.(2024) bioRxiv
- PubMed: 38798381
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.05.10.593593
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8VEG, 8VGE, 8VGF, 8VGG, 8VGH, 8VGI, 8VGJ, 8VGK, 8VGL, 8VGM, 8VGN, 8VGO, 8VGP, 8VGQ - PubMed Abstract:
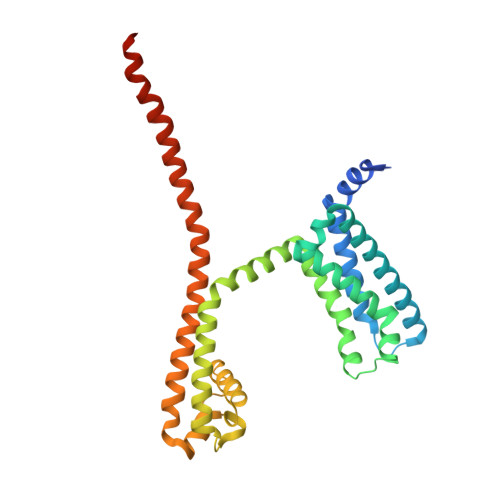
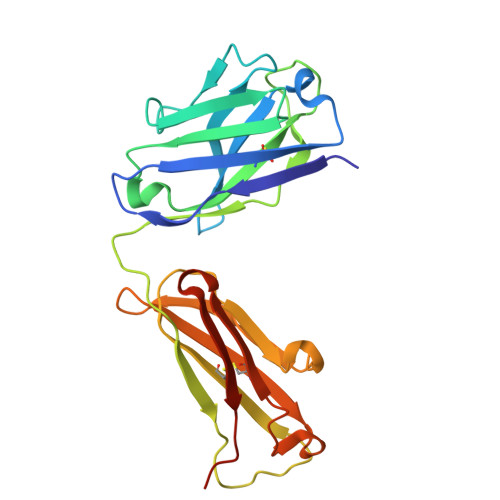
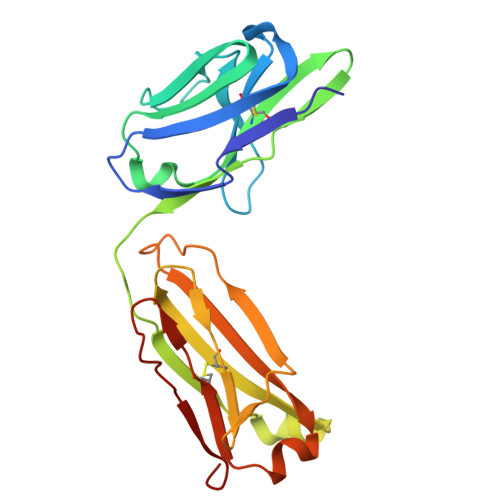
High-resolution structures of proteins are critical to understanding molecular mechanisms of biological processes and in the discovery of therapeutic molecules. Cryo-EM has revolutionized structure determination of large proteins and their complexes 1 , but a vast majority of proteins that underlie human diseases are small (< 50 kDa) and usually beyond its reach due to low signal-to-noise images and difficulties in particle alignment 2 . Current strategies to overcome this problem increase the overall size of small protein targets using scaffold proteins that bind to the target, but are limited by inherent flexibility and not being bound to their targets in a rigid manner, resulting in the target being poorly resolved compared to the scaffolds 3-11 . Here we present an iteratively engineered molecular design for transforming Fabs (antibody fragments), into conformationally rigid scaffolds (Rigid-Fabs) that, when bound to small proteins (~20 kDa), can enable high-resolution structure determination using cryo-EM. This design introduces multiple disulfide bonds at strategic locations, generates a well-folded Fab constrained into a rigid conformation and can be applied to Fabs from various species, isotypes and chimeric Fabs. We present examples of the Rigid Fab design enabling high-resolution (2.3-2.5 Å) structures of small proteins, Ang2 (26 kDa) and KRAS (21 kDa) by cryo-EM. The strategies for designing disulfide constrained Rigid Fabs in our work thus establish a general approach to overcome the target size limitation of single particle cryo-EM.
- Department of Structural Biology, Genentech Inc., South San Francisco, CA 94080, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: