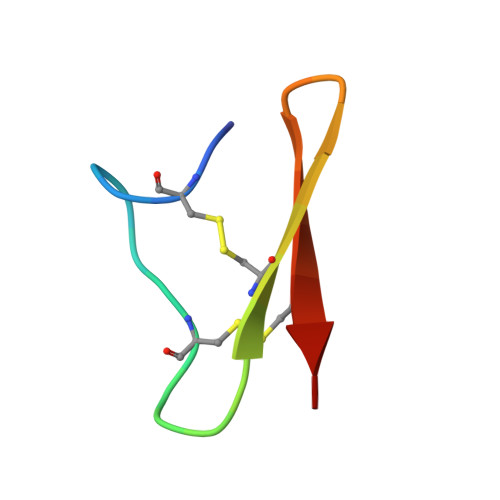
Structural analysis of an Asterias rubens peptide indicates the presence of a disulfide-directed beta-hairpin fold.
Takjoo, R., Wilson, D.T., Le Quilliec, J., Schmidt, C.A., Zhao, G., Liddell, M.J., Shaikh, N.Y., Sunagar, K., Loukas, A., Smout, M.J., Daly, N.L.(2025) FEBS Open Bio 15: 415-426
- PubMed: 39561265
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/2211-5463.13931
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8V2M, 8V2U - PubMed Abstract:
Sea stars are an abundant group of marine invertebrates that display remarkably robust regenerative capabilities throughout all life stages. Numerous proteins and peptides have been identified in a proteome study on the coelomic fluid (biofluid) of the common sea star Asterias rubens, which appear to be involved with the wound-healing response in the organism. However, the three-dimensional structure and function of several of these injury-responsive peptides, including the peptide KASH2, are yet to be investigated. Here, we show that the KASH2 peptide adopts a disulfide-directed β-hairpin fold (DDH). The DDH motif appears to be evolutionarily related to the inhibitor cystine knot motif, which is one of the most widespread disulfide-rich peptide folds. The DDH motif was originally thought to be restricted to arachnids, but our study suggests that as a result of convergent evolution it could also have originated in sea stars. Although the widely conserved DDH fold has potential cross-phyla wound-healing capacity, we have shown that KASH2 does not enhance the proliferation of human fibroblasts, a simple method for wound-healing re-epithelialisation screening. Therefore, additional research is necessary to determine the role of KASH2 in the sea stars.
- Australian Institute of Tropical Health and Medicine, James Cook University, Cairns, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: