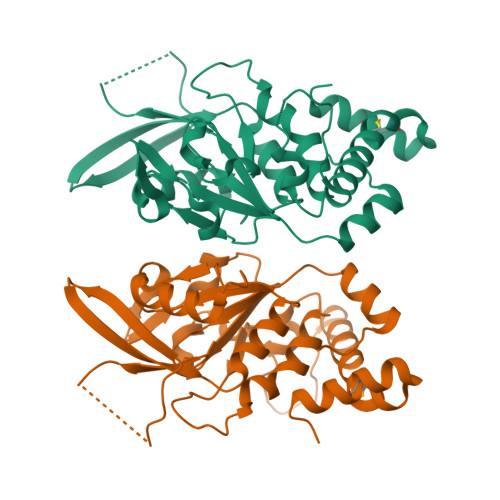
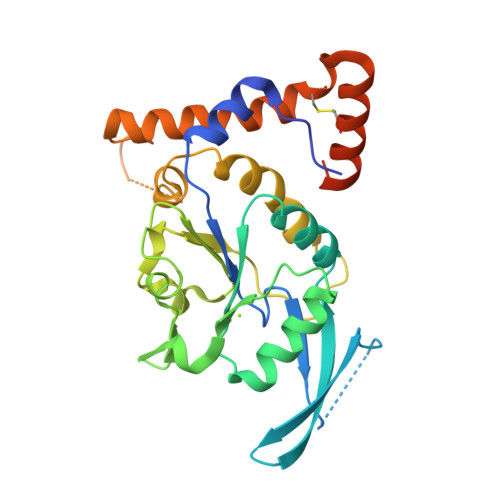
Structure and mechanism of the human CTDNEP1-NEP1R1 membrane protein phosphatase complex necessary to maintain ER membrane morphology.
Gao, S., Carrasquillo Rodriguez, J.W., Bahmanyar, S., Airola, M.V.(2024) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 121: e2321167121-e2321167121
- PubMed: 38776370
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2321167121
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8UJL, 8UJM - PubMed Abstract:
C-terminal Domain Nuclear Envelope Phosphatase 1 (CTDNEP1) is a noncanonical protein serine/threonine phosphatase that has a conserved role in regulating ER membrane biogenesis. Inactivating mutations in CTDNEP1 correlate with the development of medulloblastoma, an aggressive childhood cancer. The transmembrane protein Nuclear Envelope Phosphatase 1 Regulatory Subunit 1 (NEP1R1) binds CTDNEP1, but the molecular details by which NEP1R1 regulates CTDNEP1 function are unclear. Here, we find that knockdown of NEP1R1 generates identical phenotypes to reported loss of CTDNEP1 in mammalian cells, establishing CTDNEP1-NEP1R1 as an evolutionarily conserved membrane protein phosphatase complex that restricts ER expansion. Mechanistically, NEP1R1 acts as an activating regulatory subunit that directly binds and increases the phosphatase activity of CTDNEP1. By defining a minimal NEP1R1 domain sufficient to activate CTDNEP1, we determine high-resolution crystal structures of the CTDNEP1-NEP1R1 complex bound to a peptide sequence acting as a pseudosubstrate. Structurally, NEP1R1 engages CTDNEP1 at a site distant from the active site to stabilize and allosterically activate CTDNEP1. Substrate recognition is facilitated by a conserved Arg residue in CTDNEP1 that binds and orients the substrate peptide in the active site. Together, this reveals mechanisms for how NEP1R1 regulates CTDNEP1 and explains how cancer-associated mutations inactivate CTDNEP1.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, NY 11794.