Structural basis of the human transcriptional Mediator regulated by its dissociable kinase module.
Chao, T.C., Chen, S.F., Kim, H.J., Tang, H.C., Tseng, H.C., Xu, A., Palao 3rd, L., Khadka, S., Li, T., Huang, M.F., Lee, D.F., Murakami, K., Boyer, T.G., Tsai, K.L.(2024) Mol Cell 84: 3932-3949.e10
- PubMed: 39321804
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2024.09.001
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8TQ2, 8TQC, 8TQW, 8TRH - PubMed Abstract:
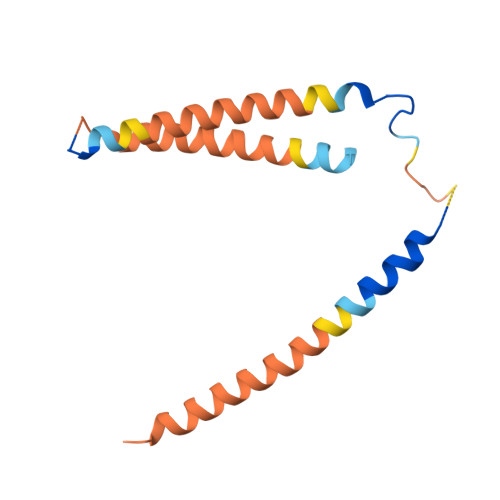
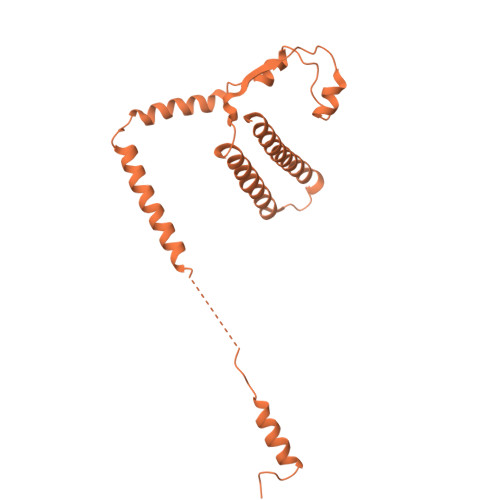
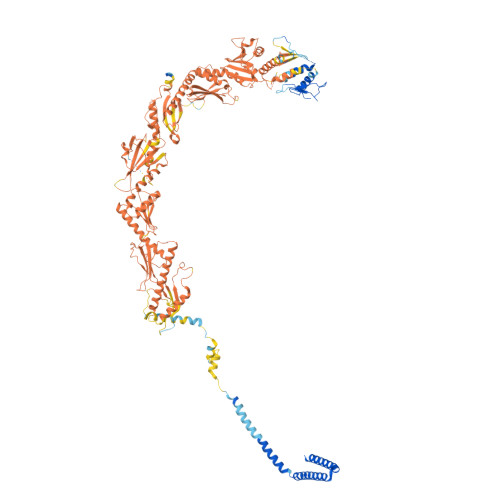
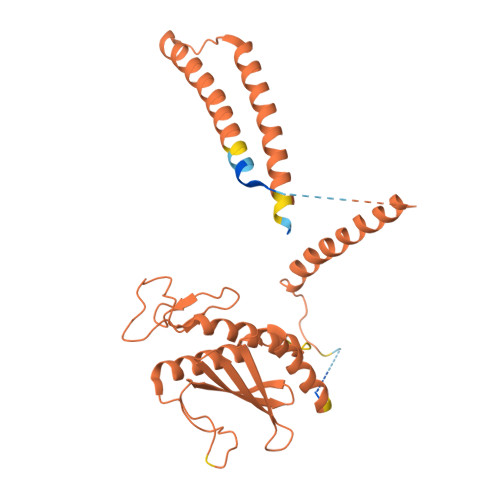
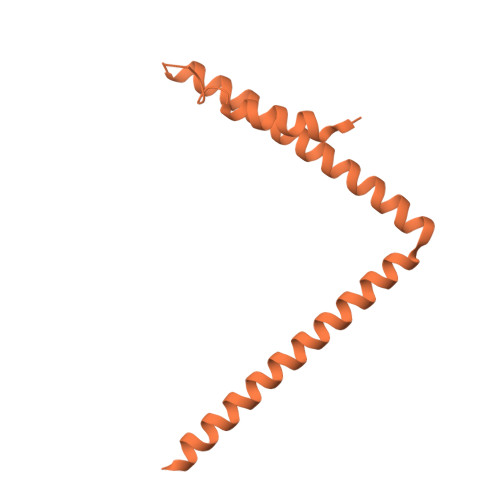
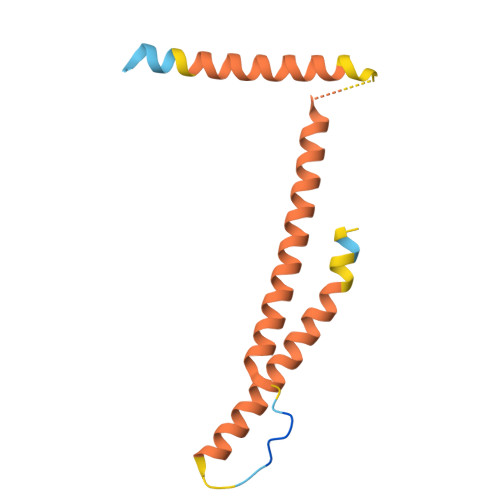
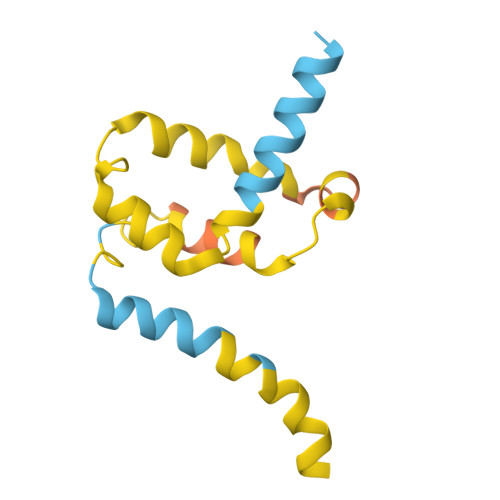
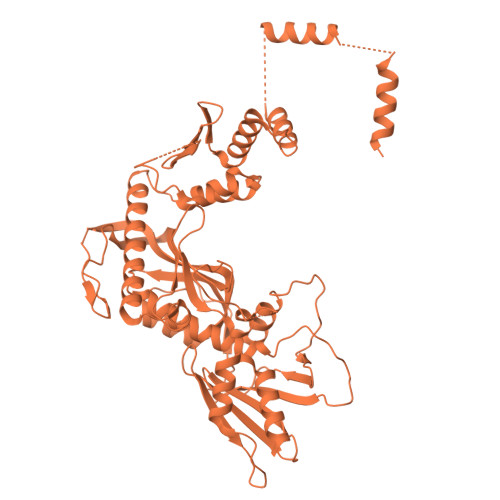
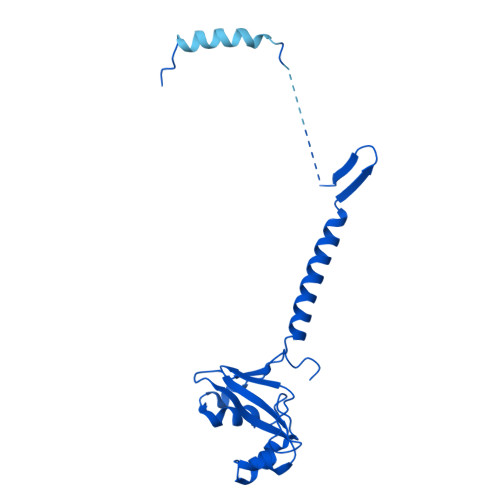
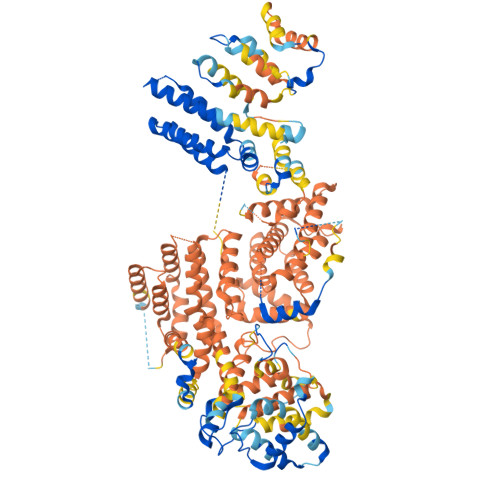
The eukaryotic transcriptional Mediator comprises a large core (cMED) and a dissociable CDK8 kinase module (CKM). cMED recruits RNA polymerase II (RNA Pol II) and promotes pre-initiation complex formation in a manner repressed by the CKM through mechanisms presently unknown. Herein, we report cryoelectron microscopy structures of the complete human Mediator and its CKM. The CKM binds to multiple regions on cMED through both MED12 and MED13, including a large intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in the latter. MED12 and MED13 together anchor the CKM to the cMED hook, positioning CDK8 downstream and proximal to the transcription start site. Notably, the MED13 IDR obstructs the recruitment of RNA Pol II/MED26 onto cMED by direct occlusion of their respective binding sites, leading to functional repression of cMED-dependent transcription. Combined with biochemical and functional analyses, these structures provide a conserved mechanistic framework to explain the basis for CKM-mediated repression of cMED function.
- Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, McGovern Medical School, University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, Houston, TX, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: