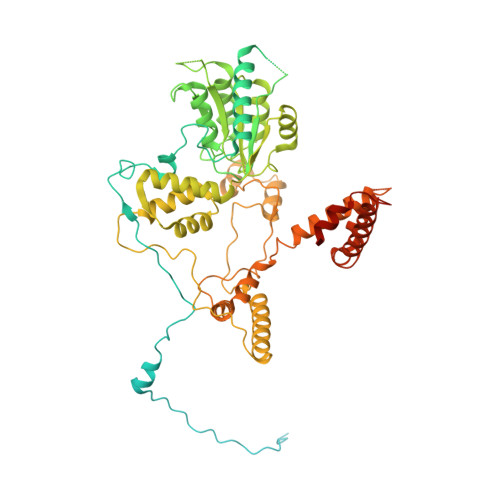
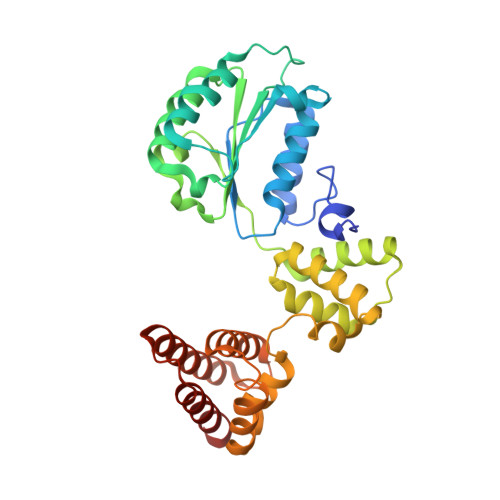
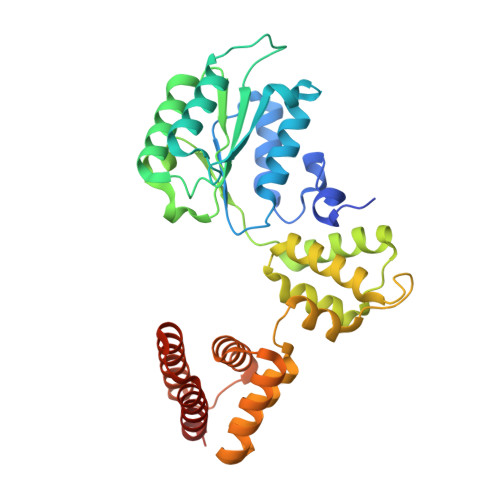
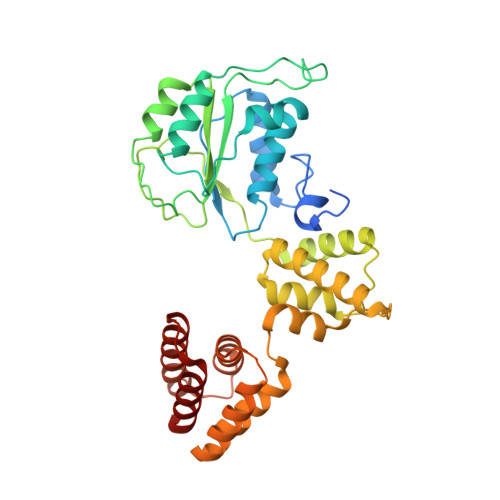
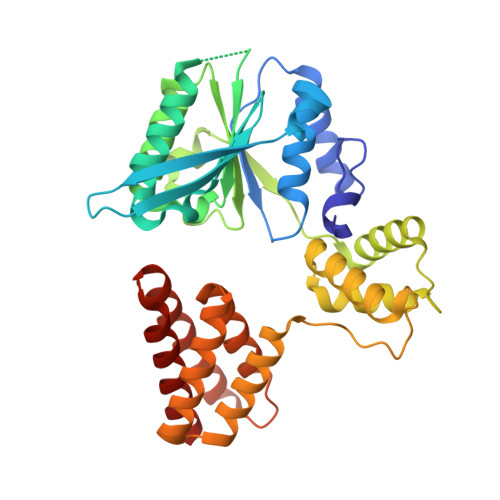
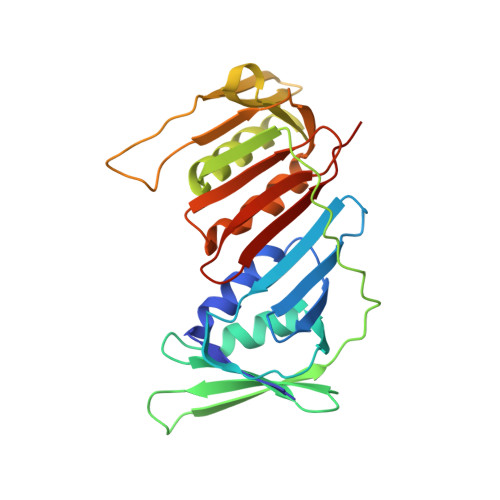
Structure of the PCNA unloader Elg1-RFC.
Zheng, F., Yao, N.Y., Georgescu, R.E., Li, H., O'Donnell, M.E.(2024) Sci Adv 10: eadl1739-eadl1739
- PubMed: 38427736
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adl1739
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8THB, 8THC, 8THD - PubMed Abstract:
During DNA replication, the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) clamps are loaded onto primed sites for each Okazaki fragment synthesis by the AAA + heteropentamer replication factor C (RFC). PCNA encircling duplex DNA is quite stable and is removed from DNA by the dedicated clamp unloader Elg1-RFC. Here, we show the cryo-EM structure of Elg1-RFC in various states with PCNA. The structures reveal essential features of Elg1-RFC that explain how it is dedicated to PCNA unloading. Specifically, Elg1 contains two external loops that block opening of the Elg1-RFC complex for DNA binding, and an "Elg1 plug" domain that fills the central DNA binding chamber, thereby reinforcing the exclusive PCNA unloading activity of Elg1-RFC. Elg1-RFC was capable of unloading PCNA using non-hydrolyzable AMP-PNP. Both RFC and Elg1-RFC could remove PCNA from covalently closed circular DNA, indicating that PCNA unloading occurs by a mechanism that is distinct from PCNA loading. Implications for the PCNA unloading mechanism are discussed.
- Department of Structural Biology, Van Andel Institute, Grand Rapids, MI, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: