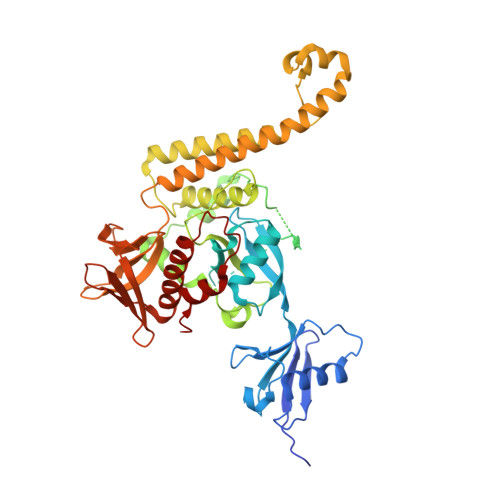
Acetyl-NPKY of integrin-beta 1 binds KINDLIN2 to control endothelial cell proliferation and junctional integrity.
Sidibe, A., Mykuliak, V.V., Zhang, P., Hytonen, V.P., Wu, J., Wehrle-Haller, B.(2024) iScience 27: 110129-110129
- PubMed: 38904068
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.110129
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8TEC, 8TEE - PubMed Abstract:
Integrin-dependent crosstalk between cell-matrix adhesions and cell-cell junctions is critical for controlling endothelial permeability and proliferation in cancer and inflammatory diseases but remains poorly understood. Here, we investigated how acetylation of the distal NPKY-motif of Integrin-β1 influences endothelial cell physiology and barrier function. Expression of an acetylation-mimetic β1-K794Q-GFP mutant led to the accumulation of immature cell-matrix adhesions accompanied by a transcriptomic reprograming of endothelial cells, involving genes associated with cell adhesion, proliferation, polarity, and barrier function. β1-K794Q-GFP induced constitutive MAPK signaling, junctional impairment, proliferation, and reduced contact inhibition at confluence. Structural analysis of Integrin-β1 interaction with KINDLIN2, biochemical pulldown assay, and binding energy determination by using molecular dynamics simulation showed that acetylation of K794 and the K794Q-mutant increased KINDLIN2 binding affinity to the Integrin-β1. Thus, enhanced recruitment of KINDLIN2 to Lysine-acetylated Integrin-β1 and resulting modulation of barrier function, offers new therapeutic possibilities for controlling vascular permeability and disease conditions.
- Department of Cell Physiology and Metabolism, University of Geneva, Centre Médical Universitaire, Rue Michel-Servet 1, CH-1211 Geneva, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: