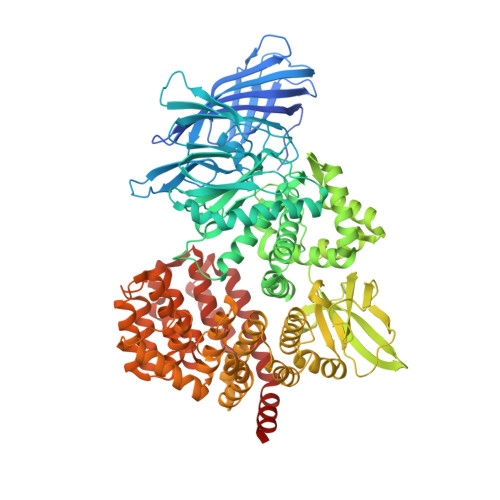
Structure of puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase and polyglutamine binding.
Madabushi, S., Chow, K.M., Song, E.S., Goswami, A., Hersh, L.B., Rodgers, D.W.(2023) PLoS One 18: e0287086-e0287086
- PubMed: 37440518
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0287086
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8SW0, 8SW1 - PubMed Abstract:
Puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase (E.C. 3.4.11.14, UniProt P55786), a zinc metallopeptidase belonging to the M1 family, degrades a number of bioactive peptides as well as peptides released from the proteasome, including polyglutamine. We report the crystal structure of PSA at 2.3 Ǻ. Overall, the enzyme adopts a V-shaped architecture with four domains characteristic of the M1 family aminopeptidases, but it is in a less compact conformation compared to most M1 enzymes of known structure. A microtubule binding sequence is present in a C-terminal HEAT repeat domain of the enzyme in a position where it might serve to mediate interaction with tubulin. In the catalytic metallopeptidase domain, an elongated active site groove lined with aromatic and hydrophobic residues and a large S1 subsite may play a role in broad substrate recognition. The structure with bound polyglutamine shows a possible interacting mode of this peptide, which is supported by mutation.
- Department of Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry and Center for Structural Biology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, Kentucky, United States of America.
Organizational Affiliation: