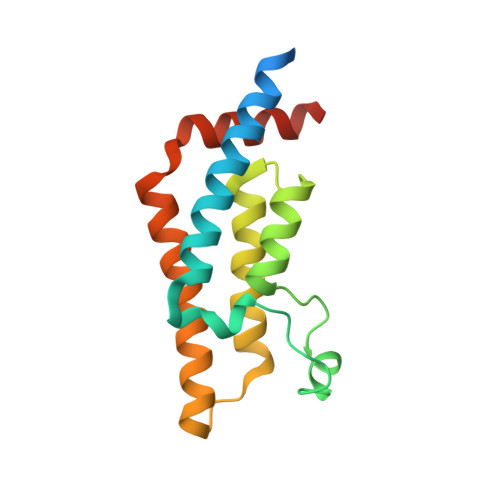
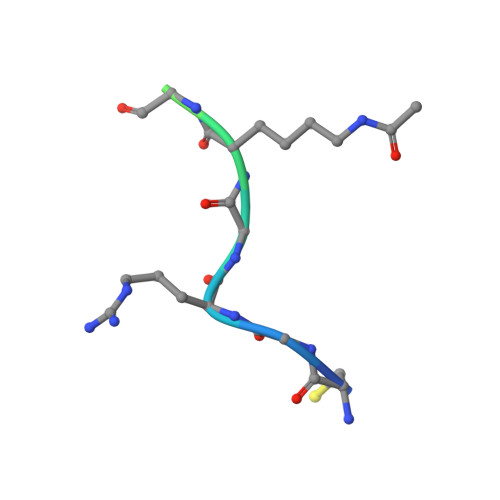
Impact of Combinatorial Histone Modifications on Acetyllysine Recognition by the ATAD2 and ATAD2B Bromodomains.
Phillips, M., Malone, K.L., Boyle, B.W., Montgomery, C., Kressy, I.A., Joseph, F.M., Bright, K.M., Boyson, S.P., Chang, S., Nix, J.C., Young, N.L., Jeffers, V., Frietze, S., Glass, K.C.(2024) J Med Chem 67: 8186-8200
- PubMed: 38733345
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00210
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8SDO, 8SDQ, 8SDX, 8UHL, 8UK5 - PubMed Abstract:
The ATPase family AAA + domain containing 2 (ATAD2) protein and its paralog ATAD2B have a C-terminal bromodomain (BRD) that functions as a reader of acetylated lysine residues on histone proteins. Using a structure-function approach, we investigated the ability of the ATAD2/B BRDs to select acetylated lysine among multiple histone post-translational modifications. The ATAD2B BRD can bind acetylated histone ligands that also contain adjacent methylation or phosphorylation marks, while the presence of these modifications significantly weakened the acetyllysine binding activity of the ATAD2 BRD. Our structural studies provide mechanistic insights into how ATAD2/B BRD-binding pocket residues coordinate the acetyllysine group in the context of adjacent post-translational modifications. Furthermore, we investigated how sequence changes in amino acids of the histone ligands impact the recognition of an adjacent acetyllysine residue. Our study highlights how the interplay between multiple combinations of histone modifications influences the reader activity of the ATAD2/B BRDs, resulting in distinct binding modes.
- Department of Pharmacology, Larner College of Medicine, University of Vermont, Burlington, Vermont 05405, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: