Discovery of a new class of bacterial heme-containing CC cleaving oxygenases.
Purwani, N.N., Rozeboom, H.J., Willers, V.P., Wijma, H.J., Fraaije, M.W.(2024) N Biotechnol 83: 82-90
- PubMed: 39053683
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2024.07.002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8S1J - PubMed Abstract:
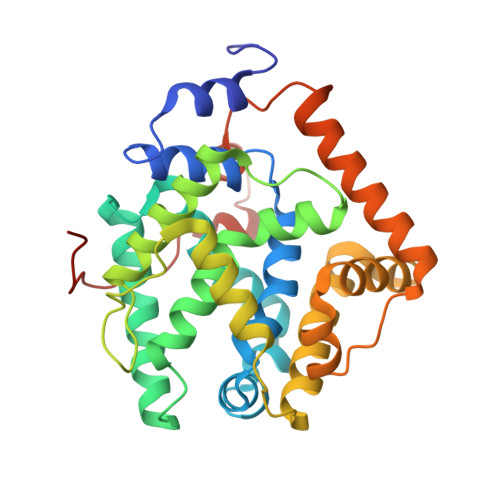
Previously, some bacteria were shown to harbour enzymes capable of catalysing the oxidative cleavage of the double bond of t-anethole and related compounds. The cofactor dependence of these enzymes remained enigmatic due to a lack of biochemical information. We report on catalytic and structural details of a representative of this group of oxidative enzymes: t-anethole oxygenase from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (TAO Sm ). The bacterial enzyme could be recombinantly expressed and purified, enabling a detailed biochemical study that has settled the dispute on its cofactor dependence. We have established that TAO Sm contains a tightly bound b-type heme and merely depends on dioxygen for catalysis. It was found to accept t-anethole, isoeugenol and O-methyl isoeugenol as substrates, all being converted into the corresponding aromatic aldehydes without the need of any cofactor regeneration. The elucidated crystal structure of TAO Sm has revealed that it contains a unique active site architecture that is conserved for this distinct class of heme-containing bacterial oxygenases. Similar to other hemoproteins, TAO Sm has a histidine (His121) as proximal ligand. Yet, unique for TAOs, an arginine (Arg89) is located at the distal axial position. Site directed mutagenesis confirmed crucial roles for these heme-liganding residues and other residues that form the substrate binding pocket. In conclusion, the results reported here reveal a new class of bacterial heme-containing oxygenases that can be used for the cleavage of alkene double bonds, analogous to ozonolysis in organic chemistry.
- Molecular Enzymology, University of Groningen, Nijenborgh 4, Groningen 9747AG, the Netherlands; Department of Health, Faculty of Vocational Studies, Kampus B Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, East Java 60286, Indonesia.
Organizational Affiliation: