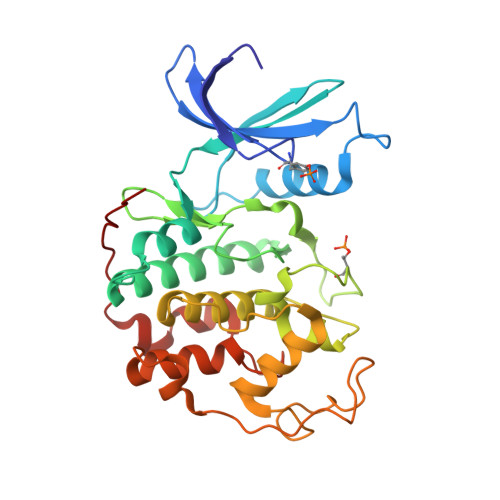
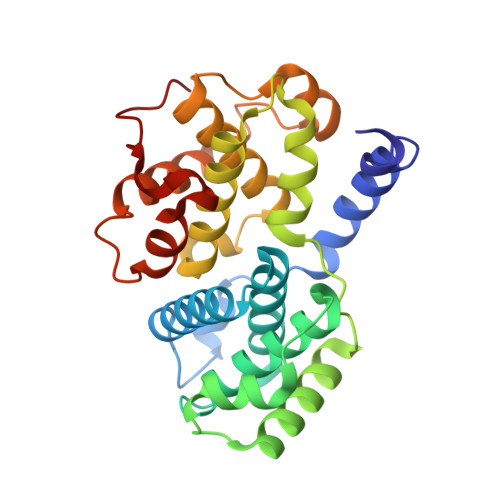
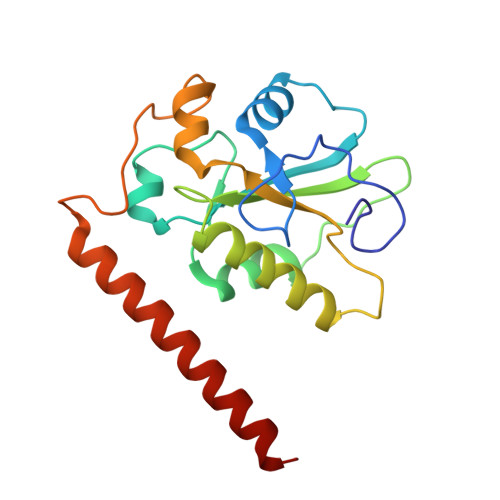
Cryo-EM structure of the CDK2-cyclin A-CDC25A complex.
Rowland, R.J., Korolchuk, S., Salamina, M., Tatum, N.J., Ault, J.R., Hart, S., Turkenburg, J.P., Blaza, J.N., Noble, M.E.M., Endicott, J.A.(2024) Nat Commun 15: 6807-6807
- PubMed: 39122719
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-51135-w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8ROZ - PubMed Abstract:
The cell division cycle 25 phosphatases CDC25A, B and C regulate cell cycle transitions by dephosphorylating residues in the conserved glycine-rich loop of CDKs to activate their activity. Here, we present the cryo-EM structure of CDK2-cyclin A in complex with CDC25A at 2.7 Å resolution, providing a detailed structural analysis of the overall complex architecture and key protein-protein interactions that underpin this 86 kDa complex. We further identify a CDC25A C-terminal helix that is critical for complex formation. Sequence conservation analysis suggests CDK1/2-cyclin A, CDK1-cyclin B and CDK2/3-cyclin E are suitable binding partners for CDC25A, whilst CDK4/6-cyclin D complexes appear unlikely substrates. A comparative structural analysis of CDK-containing complexes also confirms the functional importance of the conserved CDK1/2 GDSEID motif. This structure improves our understanding of the roles of CDC25 phosphatases in CDK regulation and may inform the development of CDC25-targeting anticancer strategies.
- Translational and Clinical Research Institute, Newcastle University Centre for Cancer, Newcastle University, Paul O'Gorman Building, Framlington Place, Newcastle upon Tyne, NE2 4HH, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: