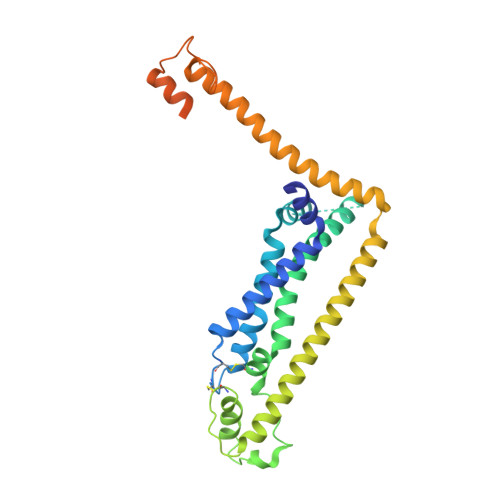
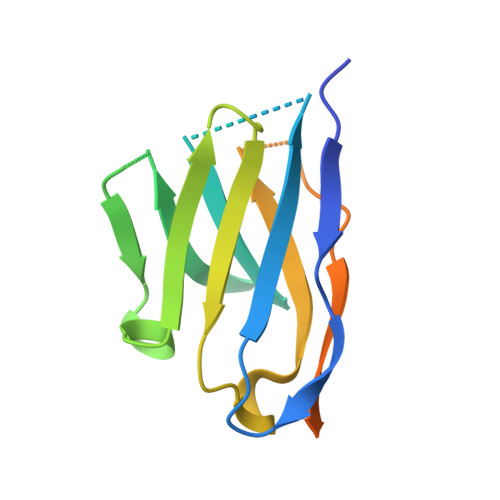
Structural features of heteromeric channels composed of CALHM2 and CALHM4 paralogs.
Drozdzyk, K., Peter, M., Dutzler, R.(2024) Elife 13
- PubMed: 38896440
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.96138
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8RMK, 8RML, 8RMM, 8RMN - PubMed Abstract:
The CALHM proteins constitute a family of large pore channels that contains six closely related paralogs in humans. Two family members, CALHM1 and 3, have been associated with the release of ATP during taste sensation. Both proteins form heteromeric channels that activate at positive potential and decreased extracellular Ca 2+ concentration. Although the structures of several family members displayed large oligomeric organizations of different size, their function has in most cases remained elusive. Our previous study has identified the paralogs CALHM2, 4 and, 6 to be highly expressed in the placenta and defined their structural properties as membrane proteins exhibiting features of large pore channels with unknown activation properties (Drożdżyk et al., 2020). Here, we investigated whether these placental paralogs would form heteromers and characterized heteromeric complexes consisting of CALHM2 and CALHM4 subunits using specific binders as fiducial markers. Both proteins assemble with different stoichiometries with the largest population containing CALHM2 as the predominant component. In these oligomers, the subunits segregate and reside in their preferred conformation found in homomeric channels. Our study has thus revealed the properties that govern the formation of CALHM heteromers in a process of potential relevance in a cellular context.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: