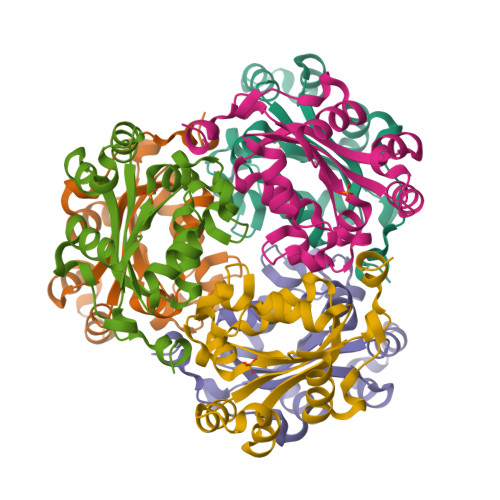
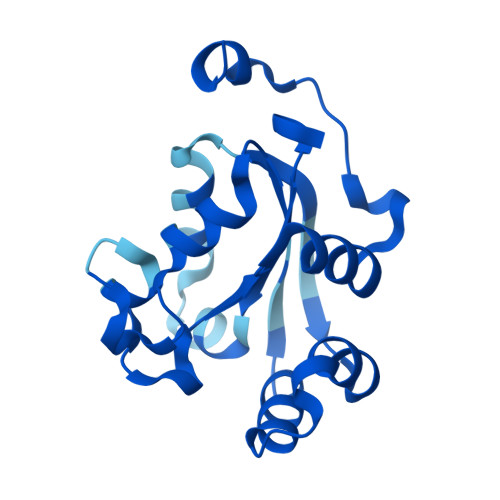
Mechanistic Insights into Substrate Recognition of Human Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase C Based on Nucleotide-Induced Structural Changes.
Amjadi, R., Werten, S., Lomada, S.K., Baldin, C., Scheffzek, K., Dunzendorfer-Matt, T., Wieland, T.(2024) Int J Mol Sci 25
- PubMed: 39337255
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25189768
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8QVY, 8QVZ, 8QW0, 8QW1, 8QW2, 8QW3 - PubMed Abstract:
Nucleoside diphosphate kinases (NDPKs) are encoded by nme genes and exist in various isoforms. Based on interactions with other proteins, they are involved in signal transduction, development and pathological processes such as tumorigenesis, metastasis and heart failure. In this study, we report a 1.25 Å resolution structure of human homohexameric NDPK-C bound to ADP and describe the yet unknown complexes formed with GDP, UDP and cAMP, all obtained at a high resolution via X-ray crystallography. Each nucleotide represents a distinct group of mono- or diphosphate purine or pyrimidine bases. We analyzed different NDPK-C nucleotide complexes in the presence and absence of Mg 2+ and explain how this ion plays an essential role in NDPKs' phosphotransferase activity. By analyzing a nucleotide-depleted NDPK-C structure, we detected conformational changes upon substrate binding and identify flexible regions in the substrate binding site. A comparison of NDPK-C with other human isoforms revealed a strong similarity in the overall composition with regard to the 3D structure, but significant differences in the charge and hydrophobicity of the isoforms' surfaces. This may play a role in isoform-specific NDPK interactions with ligands and/or important complex partners like other NDPK isoforms, as well as monomeric and heterotrimeric G proteins. Considering the recently discovered role of NDPK-C in different pathologies, these high-resolution structures thus might provide a basis for interaction studies with other proteins or small ligands, like activators or inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Molecular Biochemistry, Medical University of Innsbruck, Innrain 80/82, 6020 Innsbruck, Austria.