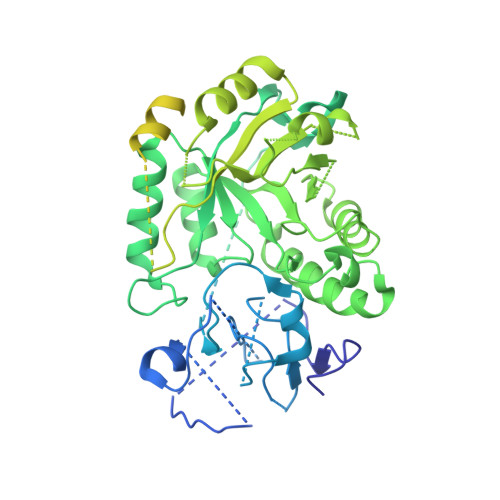
Cryo-EM of soft-landed beta-galactosidase: Gas-phase and native structures are remarkably similar.
Esser, T.K., Bohning, J., Onur, A., Chinthapalli, D.K., Eriksson, L., Grabarics, M., Fremdling, P., Konijnenberg, A., Makarov, A., Botman, A., Peter, C., Benesch, J.L.P., Robinson, C.V., Gault, J., Baker, L., Bharat, T.A.M., Rauschenbach, S.(2024) Sci Adv 10: eadl4628-eadl4628
- PubMed: 38354247
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adl4628
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8Q7Y - PubMed Abstract:
Native mass spectrometry (MS) has become widely accepted in structural biology, providing information on stoichiometry, interactions, homogeneity, and shape of protein complexes. Yet, the fundamental assumption that proteins inside the mass spectrometer retain a structure faithful to native proteins in solution remains a matter of intense debate. Here, we reveal the gas-phase structure of β-galactosidase using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) down to 2.6-Å resolution, enabled by soft landing of mass-selected protein complexes onto cold transmission electron microscopy (TEM) grids followed by in situ ice coating. We find that large parts of the secondary and tertiary structure are retained from the solution. Dehydration-driven subunit reorientation leads to consistent compaction in the gas phase. By providing a direct link between high-resolution imaging and the capability to handle and select protein complexes that behave problematically in conventional sample preparation, the approach has the potential to expand the scope of both native mass spectrometry and cryo-EM.
- Department of Chemistry, University of Oxford, South Parks Road, Oxford OX1 3QU, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: