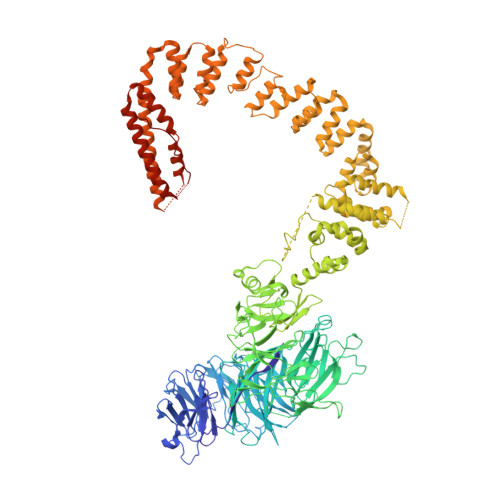
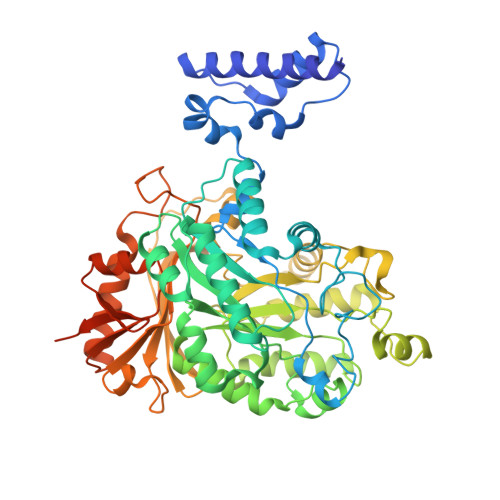
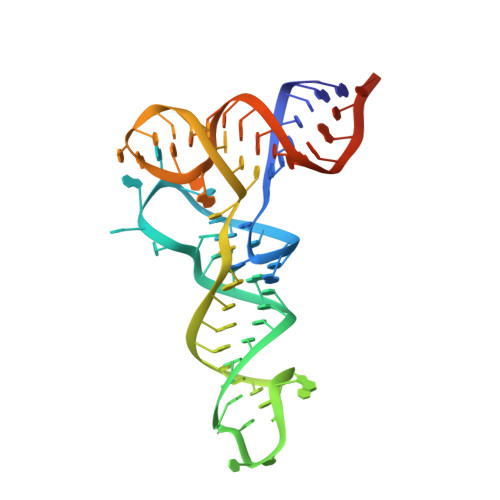
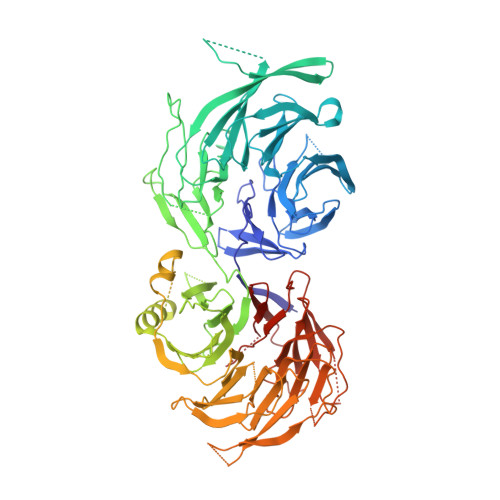Cryo-EM structures of the human Elongator complex at work.
Abbassi, N.E., Jaciuk, M., Scherf, D., Bohnert, P., Rau, A., Hammermeister, A., Rawski, M., Indyka, P., Wazny, G., Chramiec-Glabik, A., Dobosz, D., Skupien-Rabian, B., Jankowska, U., Rappsilber, J., Schaffrath, R., Lin, T.Y., Glatt, S.(2024) Nat Commun 15: 4094-4094
- PubMed: 38750017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-48251-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8PTX, 8PTY, 8PTZ, 8PU0 - PubMed Abstract:
tRNA modifications affect ribosomal elongation speed and co-translational folding dynamics. The Elongator complex is responsible for introducing 5-carboxymethyl at wobble uridine bases (cm 5 U 34 ) in eukaryotic tRNAs. However, the structure and function of human Elongator remain poorly understood. In this study, we present a series of cryo-EM structures of human ELP123 in complex with tRNA and cofactors at four different stages of the reaction. The structures at resolutions of up to 2.9 Å together with complementary functional analyses reveal the molecular mechanism of the modification reaction. Our results show that tRNA binding exposes a universally conserved uridine at position 33 (U 33 ), which triggers acetyl-CoA hydrolysis. We identify a series of conserved residues that are crucial for the radical-based acetylation of U 34 and profile the molecular effects of patient-derived mutations. Together, we provide the high-resolution view of human Elongator and reveal its detailed mechanism of action.
- Małopolska Centre of Biotechnology (MCB), Jagiellonian University, Krakow, Poland.
Organizational Affiliation: