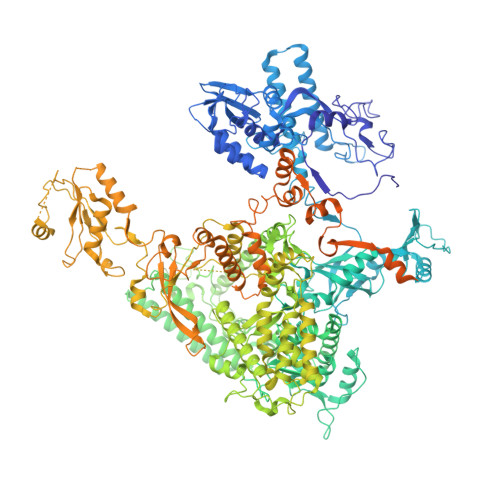
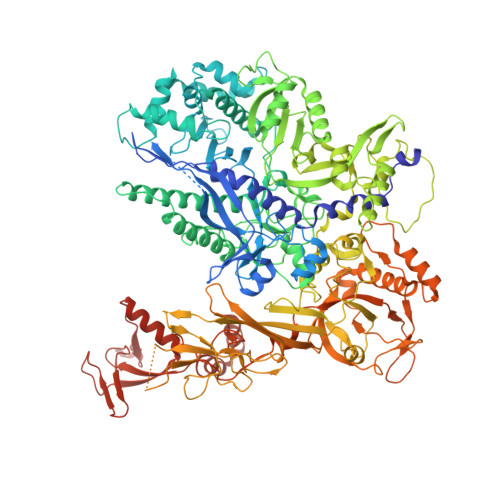
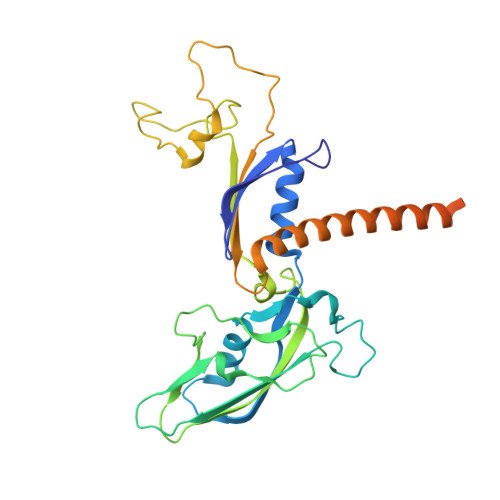
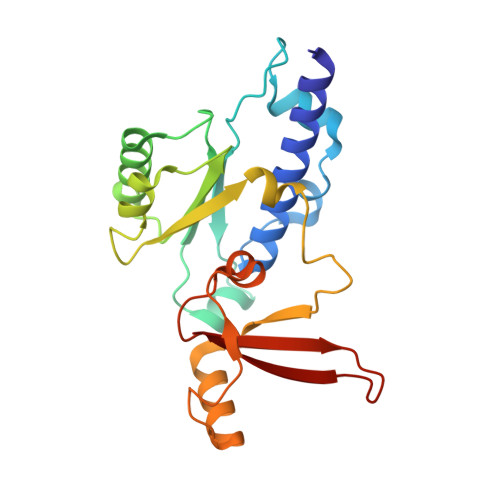
Structural basis of exoribonuclease-mediated mRNA transcription termination.
Zeng, Y., Zhang, H.W., Wu, X.X., Zhang, Y.(2024) Nature 628: 887-893
- PubMed: 38538796
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07240-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8JCH, 8K5P - PubMed Abstract:
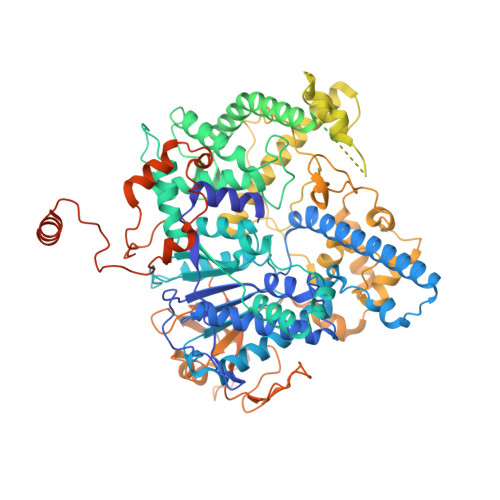
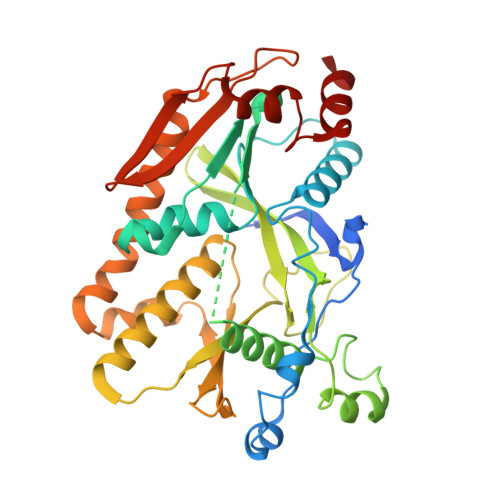
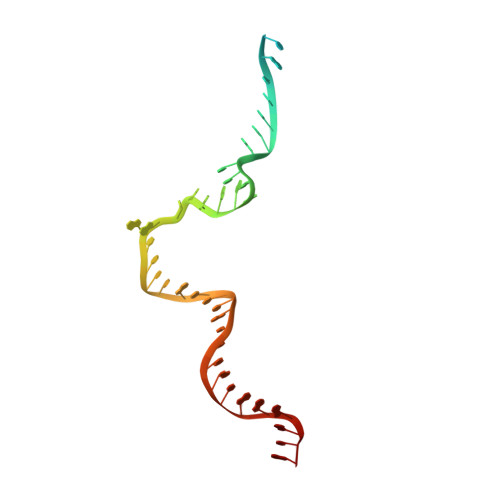
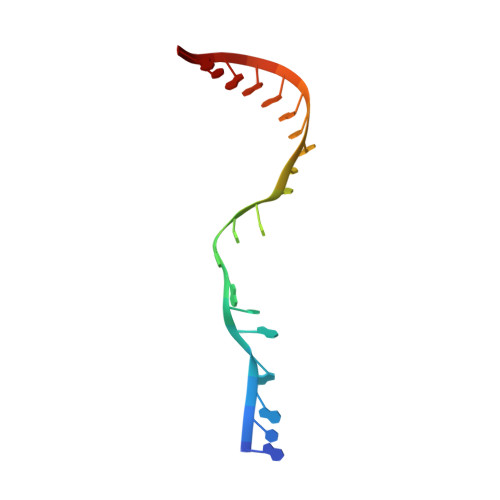
Efficient termination is required for robust gene transcription. Eukaryotic organisms use a conserved exoribonuclease-mediated mechanism to terminate the mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) 1-5 . Here we report two cryogenic electron microscopy structures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pol II pre-termination transcription complexes bound to the 5'-to-3' exoribonuclease Rat1 and its partner Rai1. Our structures show that Rat1 displaces the elongation factor Spt5 to dock at the Pol II stalk domain. Rat1 shields the RNA exit channel of Pol II, guides the nascent RNA towards its active centre and stacks three nucleotides at the 5' terminus of the nascent RNA. The structures further show that Rat1 rotates towards Pol II as it shortens RNA. Our results provide the structural mechanism for the Rat1-mediated termination of mRNA transcription by Pol II in yeast and the exoribonuclease-mediated termination of mRNA transcription in other eukaryotes.
- Key Laboratory of Synthetic Biology, National Key Laboratory of Plant Design, CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences, Shanghai Institute of Plant Physiology and Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: