Functional tailoring of a PET hydrolytic enzyme expressed in Pichia pastoris.
Li, X., Shi, B., Huang, J.W., Zeng, Z., Yang, Y., Zhang, L., Min, J., Chen, C.C., Guo, R.T.(2023) Bioresour Bioprocess 10: 26-26
- PubMed: 38647782
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-023-00648-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8IAN, 8IBI, 8IBJ - PubMed Abstract:
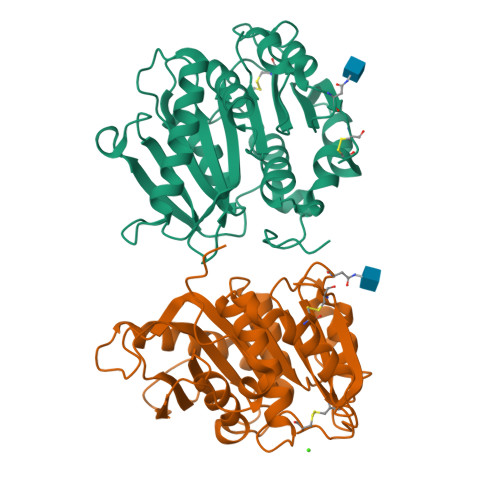
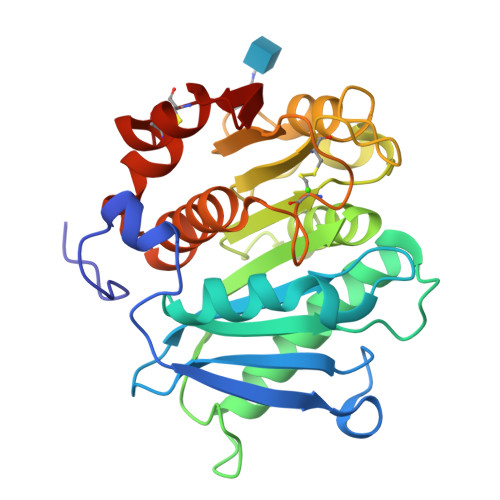
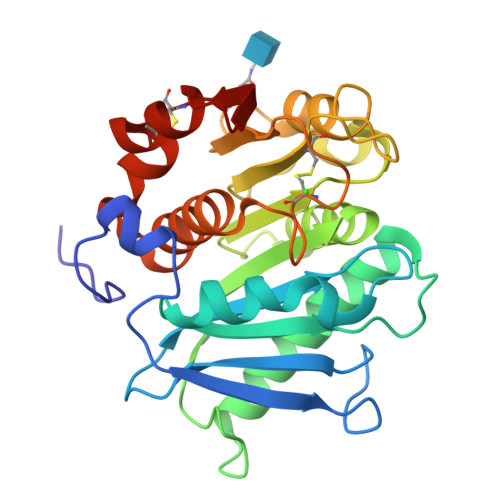
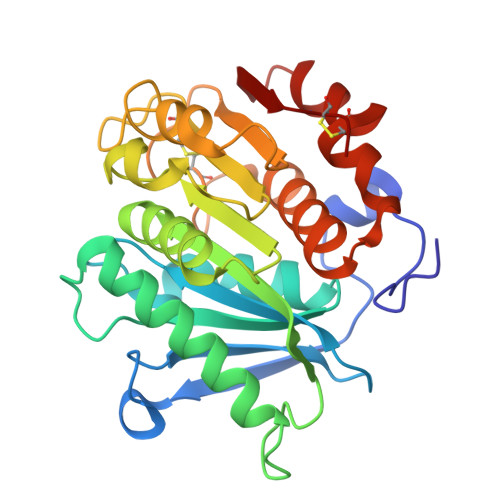
Using enzymes to hydrolyze and recycle poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) is an attractive eco-friendly approach to manage the ever-increasing PET wastes, while one major challenge to realize the commercial application of enzyme-based PET degradation is to establish large-scale production methods to produce PET hydrolytic enzyme. To achieve this goal, we exploited the industrial strain Pichia pastoris to express a PET hydrolytic enzyme from Caldimonas taiwanensis termed CtPL-DM. In contrast to the protein expressed in Escherichia coli, CtPL-DM expressed in P. pastoris is inactive in PET degradation. Structural analysis indicates that a putative N-glycosylation site N181 could restrain the conformational change of a substrate-binding Trp and hamper the enzyme action. We thus constructed N181A to remove the N-glycosylation and found that the PET hydrolytic activity of this variant was restored. The performance of N181A was further enhanced via molecular engineering. These results are of valuable in terms of PET hydrolytic enzyme production in industrial strains in the future.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Biocatalysis and Enzyme Engineering, Hubei Hongshan Laboratory, Hubei Collaborative Innovation Center for Green Transformation of Bio-Resources, Hubei Key Laboratory of Industrial Biotechnology, School of Life Sciences, Hubei University, Wuhan, 430062, People's Republic of China.