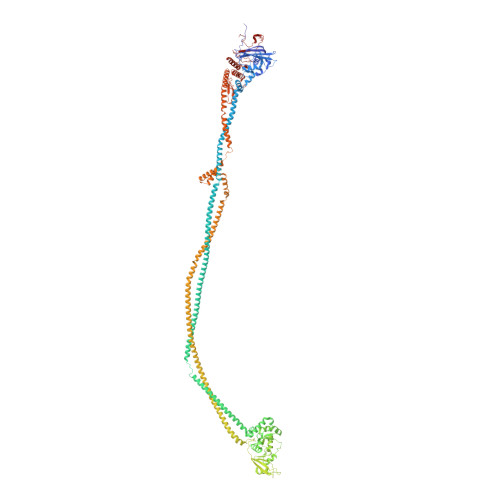
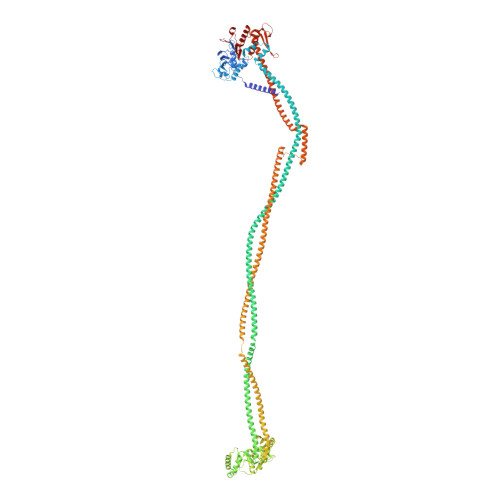
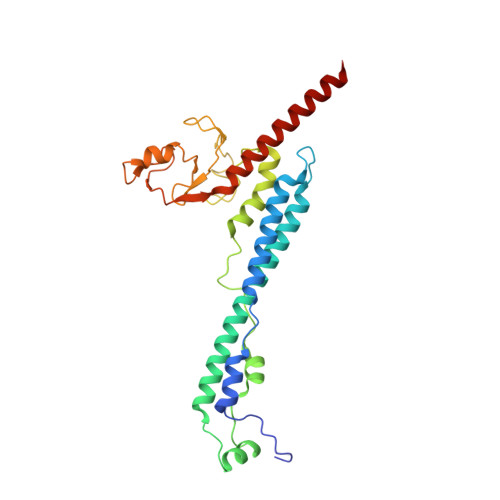
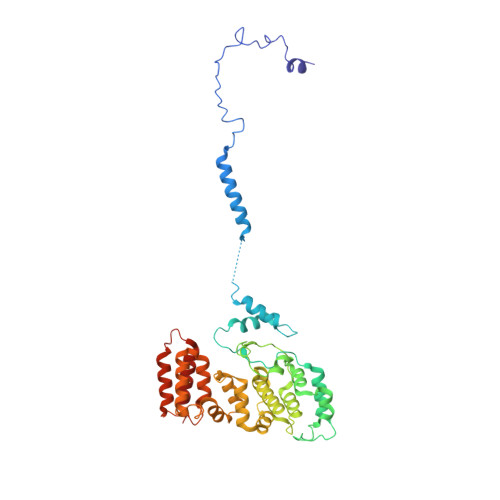
Cryo-EM structures of Smc5/6 in multiple states reveal its assembly and functional mechanisms.
Li, Q., Zhang, J., Haluska, C., Zhang, X., Wang, L., Liu, G., Wang, Z., Jin, D., Cheng, T., Wang, H., Tian, Y., Wang, X., Sun, L., Zhao, X., Chen, Z., Wang, L.(2024) Nat Struct Mol Biol 31: 1532-1542
- PubMed: 38890552
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-024-01319-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7YLM, 7YMD, 7YQH, 8HQS, 8I13, 8I21, 8I4U, 8I4V, 8I4W, 8I4X, 8WJL, 8WJN, 8WJO - PubMed Abstract:
Smc5/6 is a member of the eukaryotic structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) family of complexes with important roles in genome maintenance and viral restriction. However, limited structural understanding of Smc5/6 hinders the elucidation of its diverse functions. Here, we report cryo-EM structures of the budding yeast Smc5/6 complex in eight-subunit, six-subunit and five-subunit states. Structural maps throughout the entire length of these complexes reveal modularity and key elements in complex assembly. We show that the non-SMC element (Nse)2 subunit supports the overall shape of the complex and uses a wedge motif to aid the stability and function of the complex. The Nse6 subunit features a flexible hook region for attachment to the Smc5 and Smc6 arm regions, contributing to the DNA repair roles of the complex. Our results also suggest a structural basis for the opposite effects of the Nse1-3-4 and Nse5-6 subcomplexes in regulating Smc5/6 ATPase activity. Collectively, our integrated structural and functional data provide a framework for understanding Smc5/6 assembly and function.
- The Center for Microbes, Development and Health, CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Virology and Immunology, Shanghai Institute of Immunity and Infection, Chinese Academy of Sciences,University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: