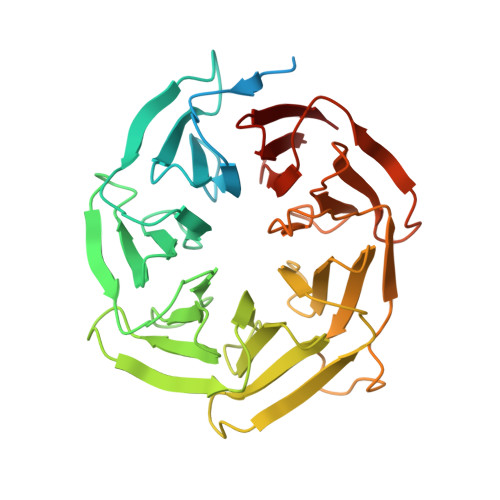
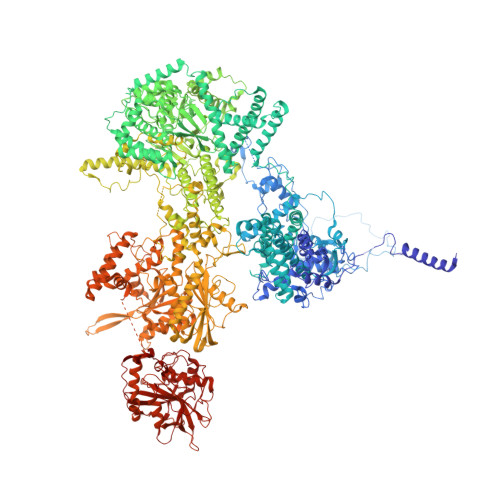
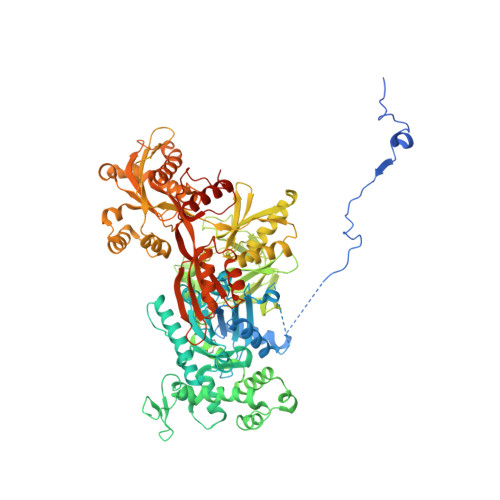
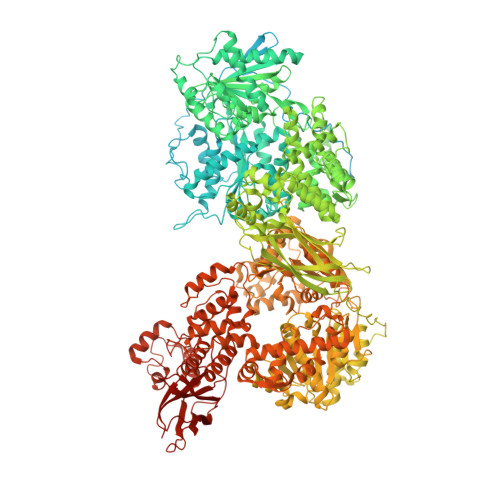
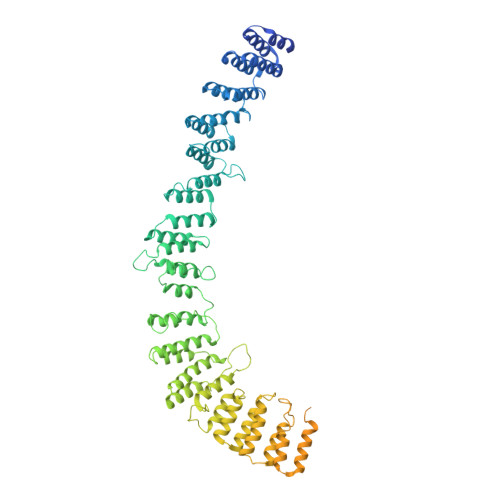
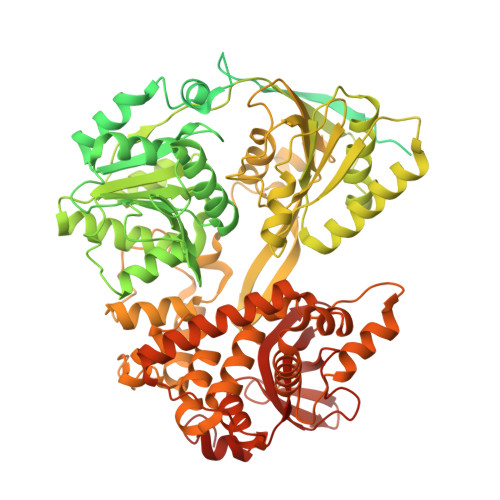
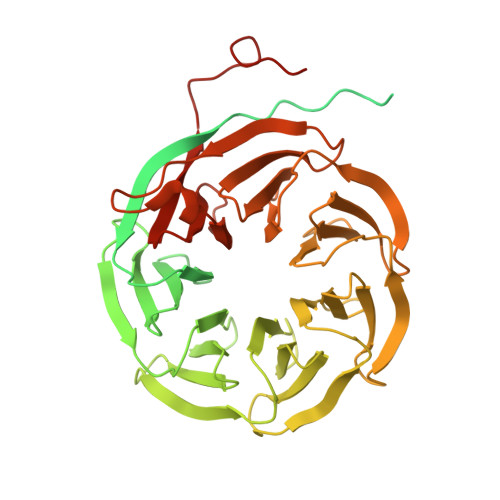
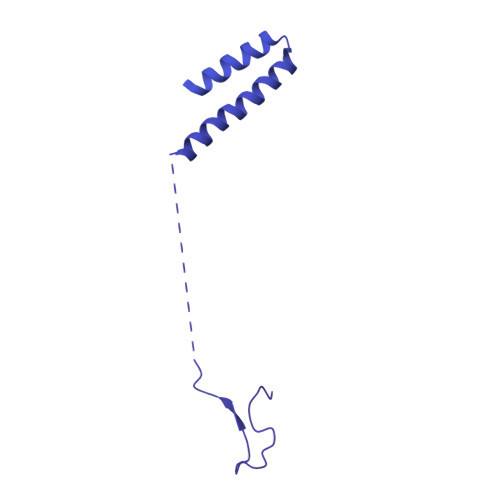
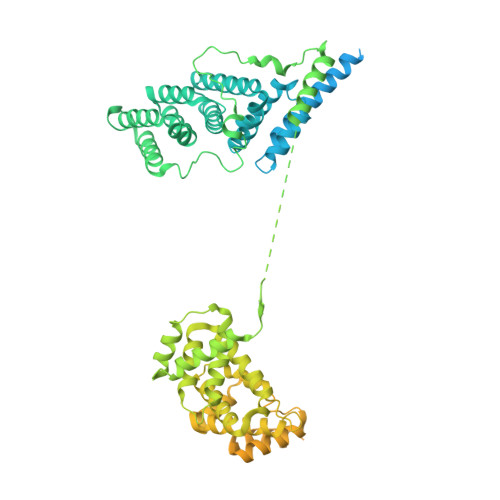
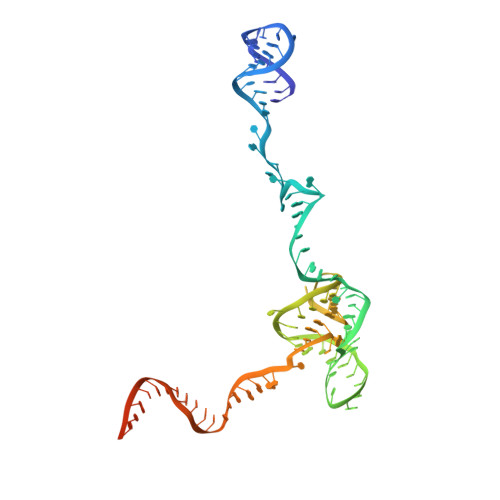
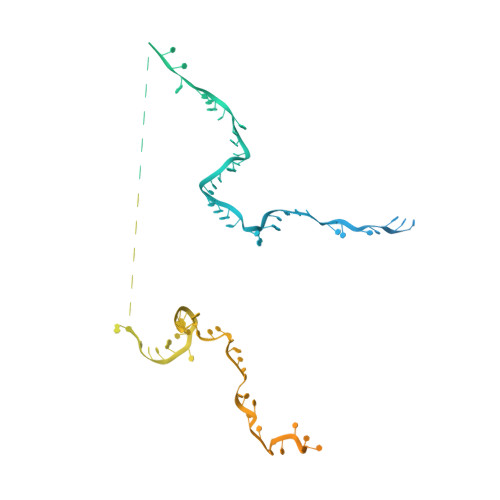
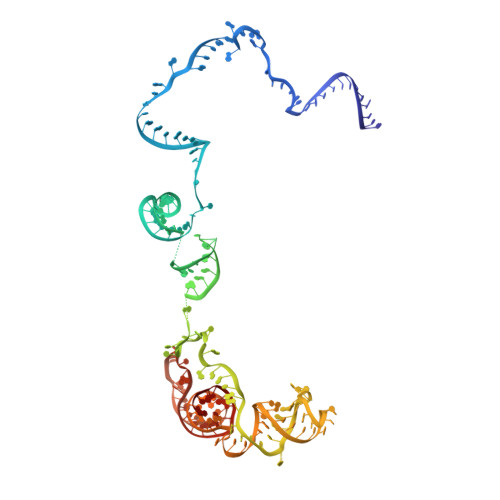
Molecular basis for the activation of human spliceosome.
Zhan, X., Lu, Y., Shi, Y.(2024) Nat Commun 15: 6348-6348
- PubMed: 39068178
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-50785-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8I0P, 8I0R, 8I0S, 8I0T, 8I0U, 8I0V, 8I0W - PubMed Abstract:
The spliceosome executes pre-mRNA splicing through four sequential stages: assembly, activation, catalysis, and disassembly. Activation of the spliceosome, namely remodeling of the pre-catalytic spliceosome (B complex) into the activated spliceosome (B act complex) and the catalytically activated spliceosome (B * complex), involves major flux of protein components and structural rearrangements. Relying on a splicing inhibitor, we have captured six intermediate states between the B and B * complexes: pre-B act , B act -I, B act -II, B act -III, B act -IV, and post-B act . Their cryo-EM structures, together with an improved structure of the catalytic step I spliceosome (C complex), reveal how the catalytic center matures around the internal stem loop of U6 snRNA, how the branch site approaches 5'-splice site, how the RNA helicase PRP2 rearranges to bind pre-mRNA, and how U2 snRNP undergoes remarkable movement to facilitate activation. We identify a previously unrecognized key role of PRP2 in spliceosome activation. Our study recapitulates a molecular choreography of the human spliceosome during its catalytic activation.
- Westlake Laboratory of Life Sciences and Biomedicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China. zhanxiechao@westlake.edu.cn.
Organizational Affiliation: