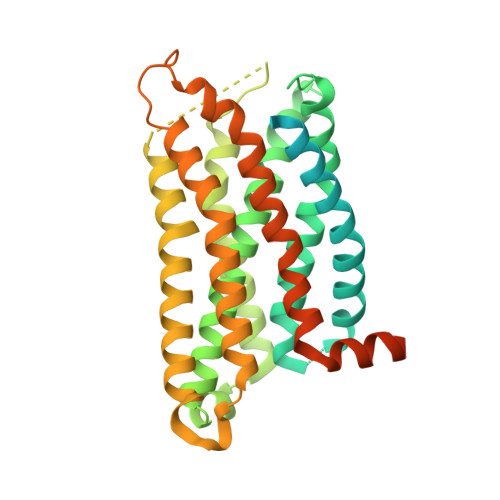
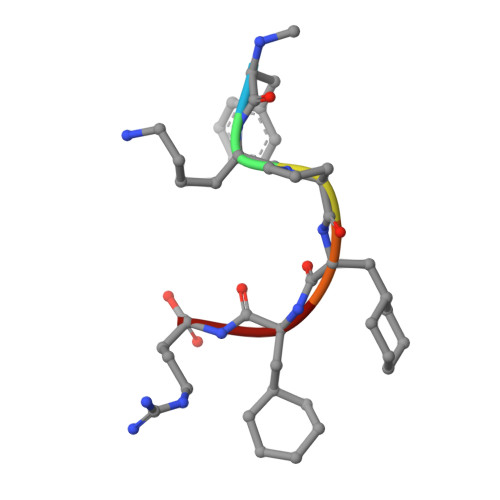
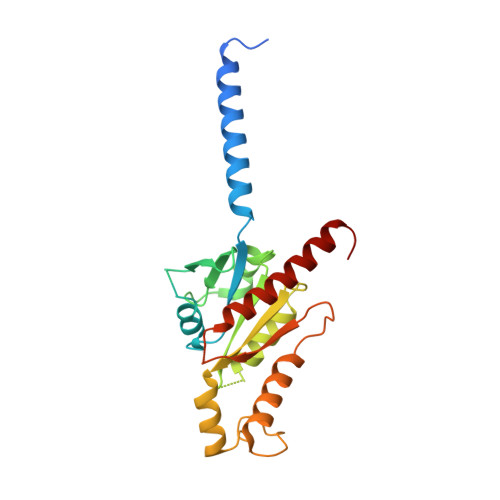
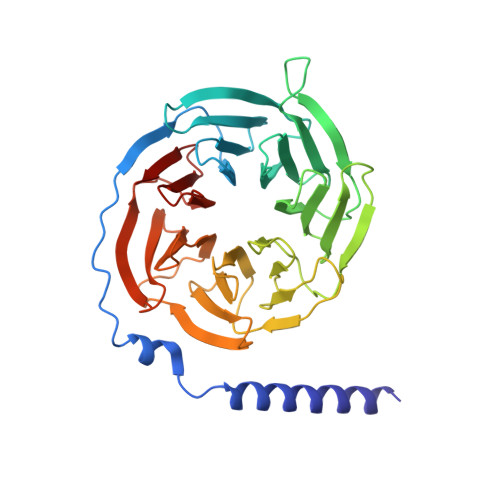
Molecular basis of anaphylatoxin binding, activation, and signaling bias at complement receptors.
Yadav, M.K., Maharana, J., Yadav, R., Saha, S., Sarma, P., Soni, C., Singh, V., Saha, S., Ganguly, M., Li, X.X., Mohapatra, S., Mishra, S., Khant, H.A., Chami, M., Woodruff, T.M., Banerjee, R., Shukla, A.K., Gati, C.(2023) Cell 186: 4956-4973.e21
- PubMed: 37852260
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2023.09.020
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8HPT, 8HQC, 8I95, 8I97, 8I9A, 8I9L, 8I9S, 8IA2, 8J6D, 8JZZ - PubMed Abstract:
The complement system is a critical part of our innate immune response, and the terminal products of this cascade, anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a, exert their physiological and pathophysiological responses primarily via two GPCRs, C3aR and C5aR1. However, the molecular mechanism of ligand recognition, activation, and signaling bias of these receptors remains mostly elusive. Here, we present nine cryo-EM structures of C3aR and C5aR1 activated by their natural and synthetic agonists, which reveal distinct binding pocket topologies of complement anaphylatoxins and provide key insights into receptor activation and transducer coupling. We also uncover the structural basis of a naturally occurring mechanism to dampen the inflammatory response of C5a via proteolytic cleavage of the terminal arginine and the G-protein signaling bias elicited by a peptide agonist of C3aR identified here. In summary, our study elucidates the innerworkings of the complement anaphylatoxin receptors and should facilitate structure-guided drug discovery to target these receptors in a spectrum of disorders.
- Department of Biological Sciences and Bioengineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur 208016, India.
Organizational Affiliation: