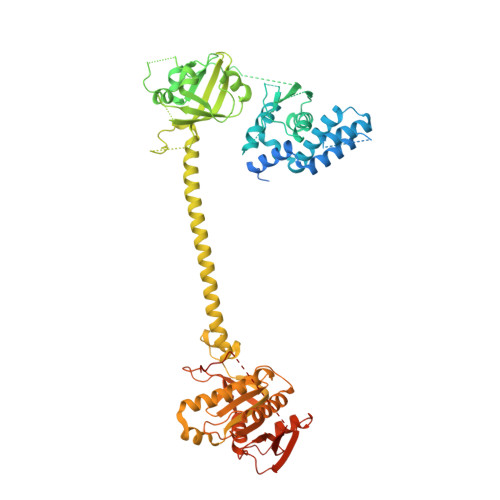
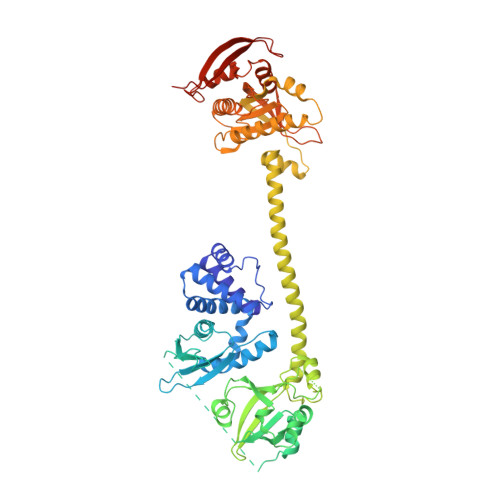
NO binds to the distal site of haem in the fully activated soluble guanylate cyclase.
Liu, R., Kang, Y., Chen, L.(2023) Nitric Oxide 134-135: 17-22
- PubMed: 36972843
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2023.03.002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8HBE, 8HBF, 8HBH - PubMed Abstract:
Soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) is the primary receptor for nitric oxide (NO). The binding of NO to the haem of sGC induces a large conformational change in the enzyme and activates its cyclase activity. However, whether NO binds to the proximal site or the distal site of haem in the fully activated state remains under debate. Here, we present cryo-EM maps of sGC in the NO-activated state at high resolutions, allowing the observation of the density of NO. These cryo-EM maps show the binding of NO to the distal site of haem in the NO-activated state.
- State Key Laboratory of Membrane Biology, College of Future Technology, Institute of Molecular Medicine, Peking University, Beijing Key Laboratory of Cardiometabolic Molecular Medicine, Beijing, 100871, China; National Biomedical Imaging Center, Peking University, Beijing, 100871, China.
Organizational Affiliation: