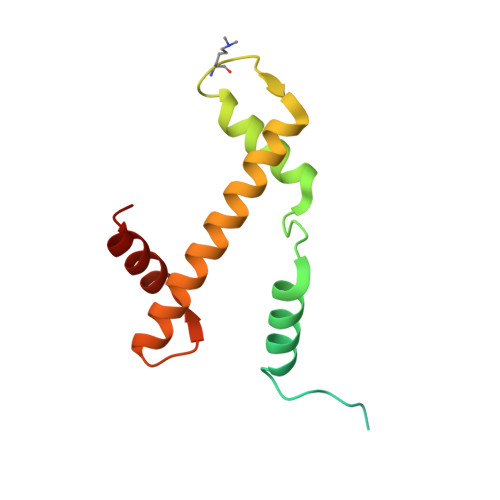
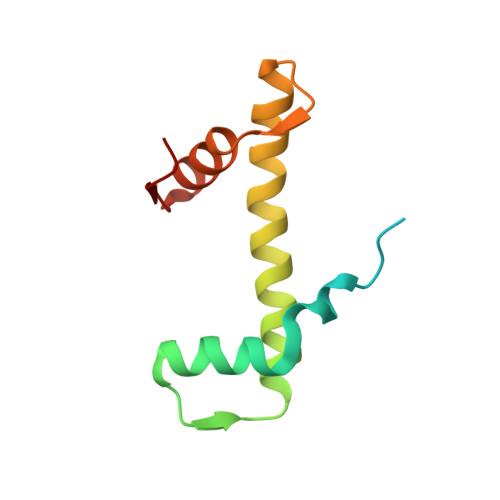
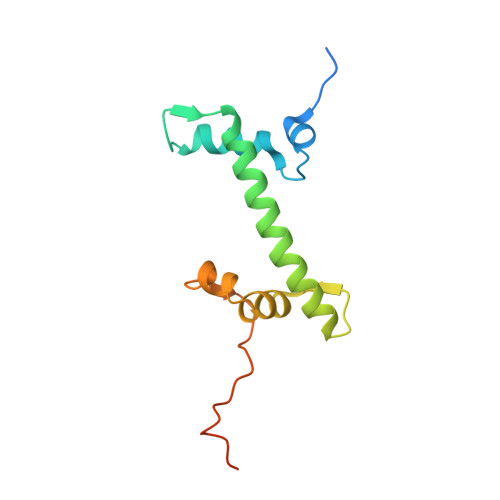
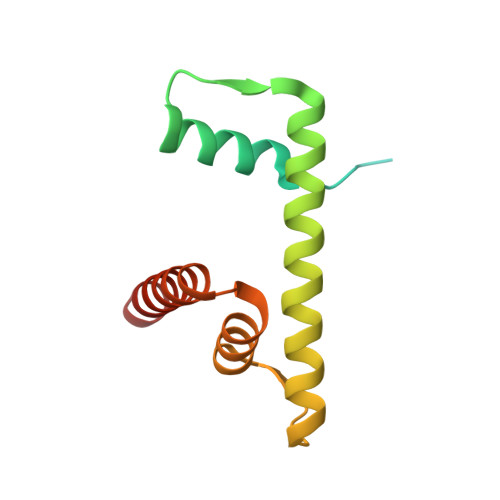
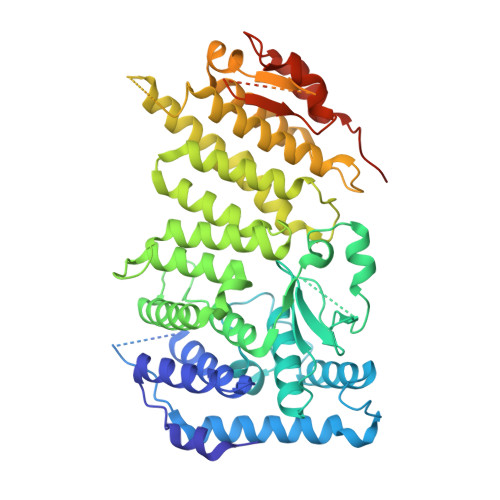
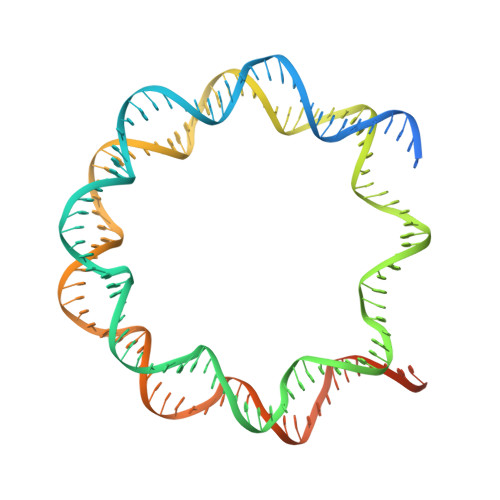
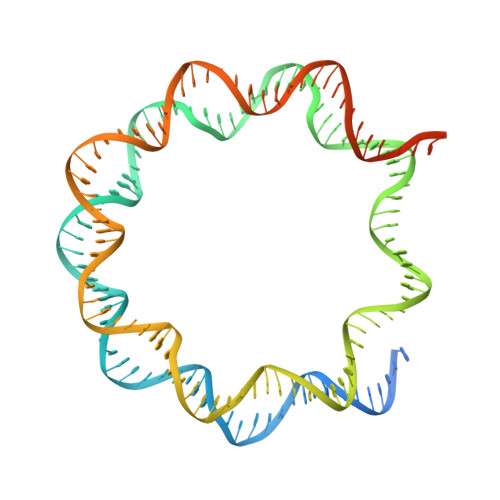
Menin "reads" H3K79me2 mark in a nucleosomal context.
Lin, J., Wu, Y., Tian, G., Yu, D., Yang, E., Lam, W.H., Liu, Z., Jing, Y., Dang, S., Bao, X., Wong, J.W.H., Zhai, Y., Li, X.D.(2023) Science 379: 717-723
- PubMed: 36795828
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adc9318
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8GPN - PubMed Abstract:
Methylation of histone H3 lysine-79 (H3K79) is an epigenetic mark for gene regulation in development, cellular differentiation, and disease progression. However, how this histone mark is translated into downstream effects remains poorly understood owing to a lack of knowledge about its readers. We developed a nucleosome-based photoaffinity probe to capture proteins that recognize H3K79 dimethylation (H3K79me2) in a nucleosomal context. In combination with a quantitative proteomics approach, this probe identified menin as a H3K79me2 reader. A cryo-electron microscopy structure of menin bound to an H3K79me2 nucleosome revealed that menin engages with the nucleosome using its fingers and palm domains and recognizes the methylation mark through a π-cation interaction. In cells, menin is selectively associated with H3K79me2 on chromatin, particularly in gene bodies.
- Department of Chemistry, University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China.
Organizational Affiliation: