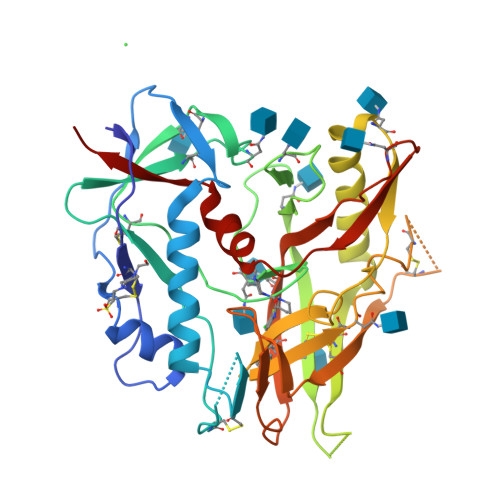
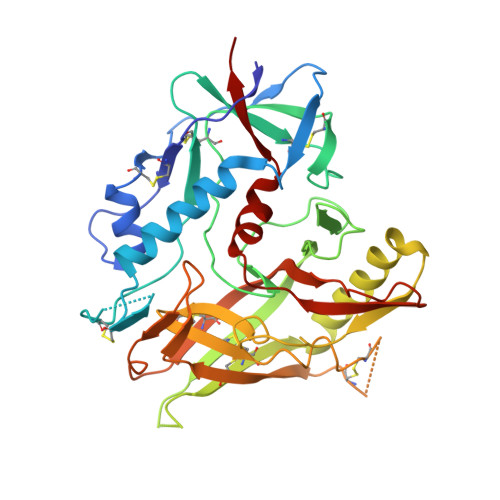
Piperidine CD4-Mimetic Compounds Expose Vulnerable Env Epitopes Sensitizing HIV-1-Infected Cells to ADCC.
Ding, S., Tolbert, W.D., Zhu, H., Lee, D., Marchitto, L., Higgins, T., Zhao, X., Nguyen, D., Sherburn, R., Richard, J., Gendron-Lepage, G., Medjahed, H., Mohammadi, M., Abrams, C., Pazgier, M., Smith III, A.B., Finzi, A.(2023) Viruses 15
- PubMed: 37243271
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051185
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8GCZ, 8GD0, 8GD1, 8GD3, 8GD5, 8GJT - PubMed Abstract:
The ability of the HIV-1 accessory proteins Nef and Vpu to decrease CD4 levels contributes to the protection of infected cells from antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) by preventing the exposure of Env vulnerable epitopes. Small-molecule CD4 mimetics (CD4mc) based on the indane and piperidine scaffolds such as (+)-BNM-III-170 and ( S )-MCG-IV-210 sensitize HIV-1-infected cells to ADCC by exposing CD4-induced (CD4i) epitopes recognized by non-neutralizing antibodies that are abundantly present in plasma from people living with HIV. Here, we characterize a new family of CD4mc, ( S )-MCG-IV-210 derivatives, based on the piperidine scaffold which engages the gp120 within the Phe43 cavity by targeting the highly conserved Asp 368 Env residue. We utilized structure-based approaches and developed a series of piperidine analogs with improved activity to inhibit the infection of difficult-to-neutralize tier-2 viruses and sensitize infected cells to ADCC mediated by HIV+ plasma. Moreover, the new analogs formed an H-bond with the α-carboxylic acid group of Asp 368 , opening a new avenue to enlarge the breadth of this family of anti-Env small molecules. Overall, the new structural and biological attributes of these molecules make them good candidates for strategies aimed at the elimination of HIV-1-infected cells.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre de Recherche du CHUM, Montreal, QC H2X 0A9, Canada.