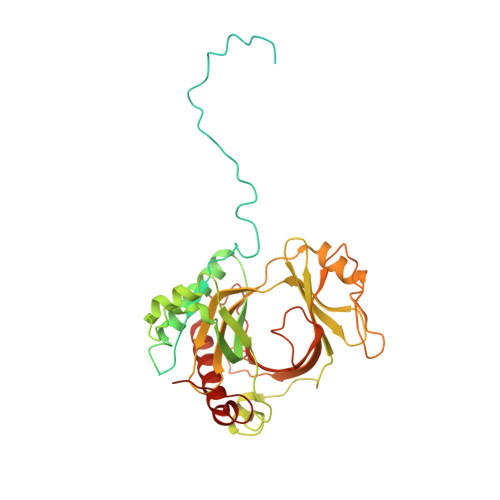
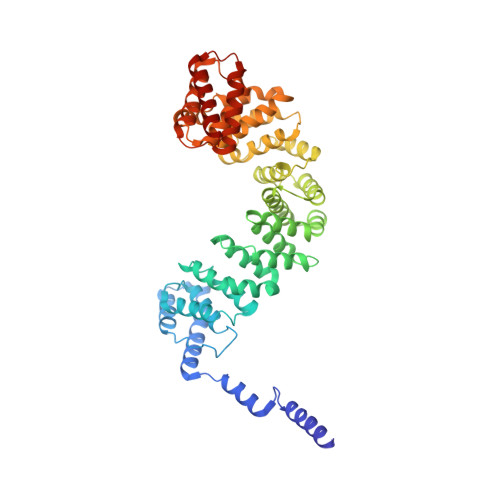
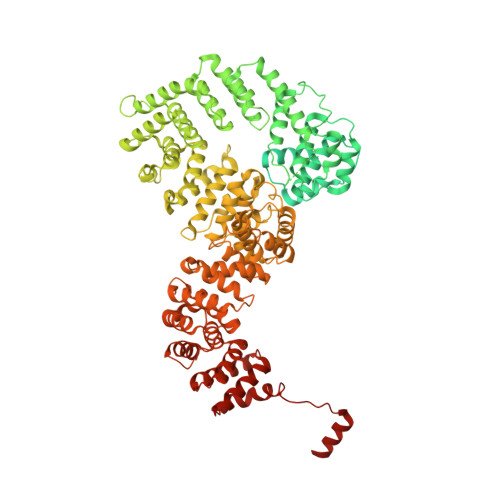
Structural basis of gRNA stabilization and mRNA recognition in trypanosomal RNA editing.
Liu, S., Wang, H., Li, X., Zhang, F., Lee, J.K.J., Li, Z., Yu, C., Hu, J.J., Zhao, X., Suematsu, T., Alvarez-Cabrera, A.L., Liu, Q., Zhang, L., Huang, L., Aphasizheva, I., Aphasizhev, R., Zhou, Z.H.(2023) Science 381: eadg4725-eadg4725
- PubMed: 37410820
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adg4725
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8FN4, 8FN6, 8FNC, 8FNF, 8FNI, 8FNK - PubMed Abstract:
In Trypanosoma brucei , the editosome, composed of RNA-editing substrate-binding complex (RESC) and RNA-editing catalytic complex (RECC), orchestrates guide RNA (gRNA)-programmed editing to recode cryptic mitochondrial transcripts into messenger RNAs (mRNAs). The mechanism of information transfer from gRNA to mRNA is unclear owing to a lack of high-resolution structures for these complexes. With cryo-electron microscopy and functional studies, we have captured gRNA-stabilizing RESC-A and gRNA-mRNA-binding RESC-B and RESC-C particles. RESC-A sequesters gRNA termini, thus promoting hairpin formation and blocking mRNA access. The conversion of RESC-A into RESC-B or -C unfolds gRNA and allows mRNA selection. The ensuing gRNA-mRNA duplex protrudes from RESC-B, likely exposing editing sites to RECC-catalyzed cleavage, uridine insertion or deletion, and ligation. Our work reveals a remodeling event facilitating gRNA-mRNA hybridization and assembly of a macromolecular substrate for the editosome's catalytic modality.
- Department of Microbiology, Immunology, and Molecular Genetics, University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: