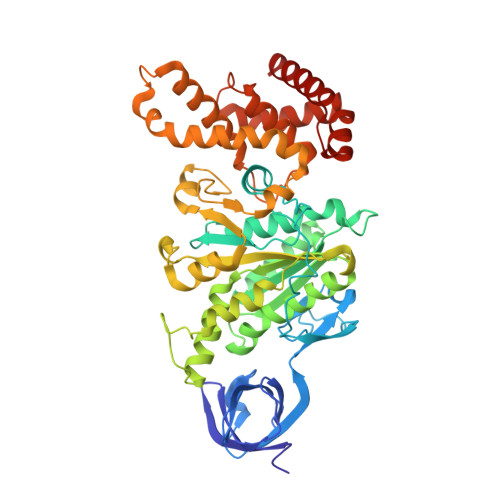
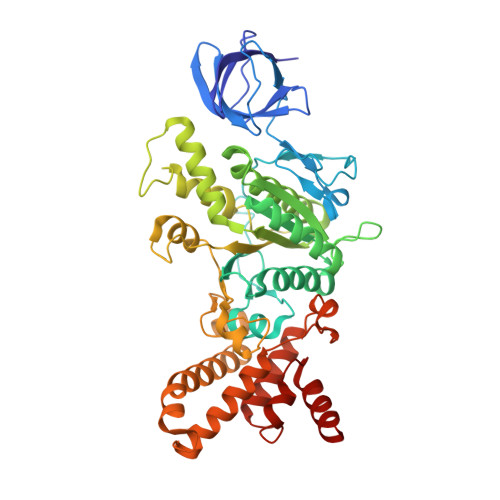
CryoEM Structure with ATP Synthase Enables Late-Stage Diversification of Cruentaren A.
Dou, X., Guo, H., D'Amico, T., Abdallah, L., Subramanian, C., Patel, B.A., Cohen, M., Rubinstein, J.L., Blagg, B.S.J.(2023) Chemistry 29: e202300262-e202300262
- PubMed: 36867738
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202300262
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8F2K - PubMed Abstract:
Cruentaren A is a natural product that exhibits potent antiproliferative activity against various cancer cell lines, yet its binding site within ATP synthase remained unknown, thus limiting the development of improved analogues as anticancer agents. Herein, we report the cryogenic electron microscopy (cryoEM) structure of cruentaren A bound to ATP synthase, which allowed the design of new inhibitors through semisynthetic modification. Examples of cruentaren A derivatives include a trans-alkene isomer, which was found to exhibit similar activity to cruentaren A against three cancer cell lines as well as several other analogues that retained potent inhibitory activity. Together, these studies provide a foundation for the generation of cruentaren A derivatives as potential therapeutics for the treatment of cancer.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, The University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, IN, 46556, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: