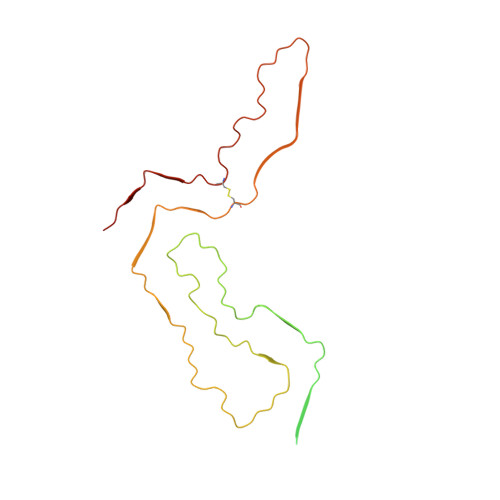
Cryo-EM of prion strains from the same genotype of host identifies conformational determinants.
Hoyt, F., Alam, P., Artikis, E., Schwartz, C.L., Hughson, A.G., Race, B., Baune, C., Raymond, G.J., Baron, G.S., Kraus, A., Caughey, B.(2022) PLoS Pathog 18: e1010947-e1010947
- PubMed: 36342968
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1010947
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8EFU - PubMed Abstract:
Prion strains in a given type of mammalian host are distinguished by differences in clinical presentation, neuropathological lesions, survival time, and characteristics of the infecting prion protein (PrP) assemblies. Near-atomic structures of prions from two host species with different PrP sequences have been determined but comparisons of distinct prion strains of the same amino acid sequence are needed to identify purely conformational determinants of prion strain characteristics. Here we report a 3.2 Å resolution cryogenic electron microscopy-based structure of the 22L prion strain purified from the brains of mice engineered to express only PrP lacking glycophosphatidylinositol anchors [anchorless (a) 22L]. Comparison of this near-atomic structure to our recently determined structure of the aRML strain propagated in the same inbred mouse reveals that these two mouse prion strains have distinct conformational templates for growth via incorporation of PrP molecules of the same sequence. Both a22L and aRML are assembled as stacks of PrP molecules forming parallel in-register intermolecular β-sheets and intervening loops, with single monomers spanning the ordered fibril core. Each monomer shares an N-terminal steric zipper, three major arches, and an overall V-shape, but the details of these and other conformational features differ markedly. Thus, variations in shared conformational motifs within a parallel in-register β-stack fibril architecture provide a structural basis for prion strain differentiation within a single host genotype.
- Research Technologies Branch, Rocky Mountain Laboratories, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Hamilton, Montana, United States of America.
Organizational Affiliation: