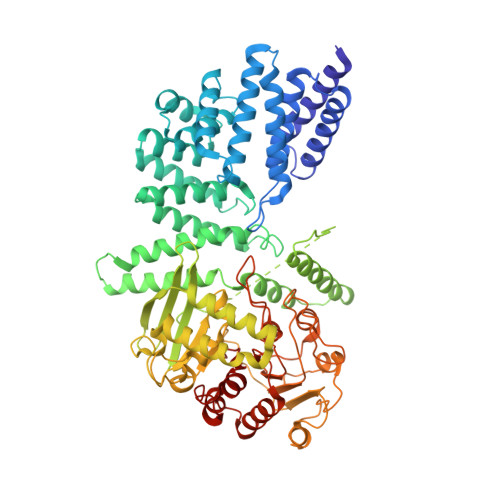
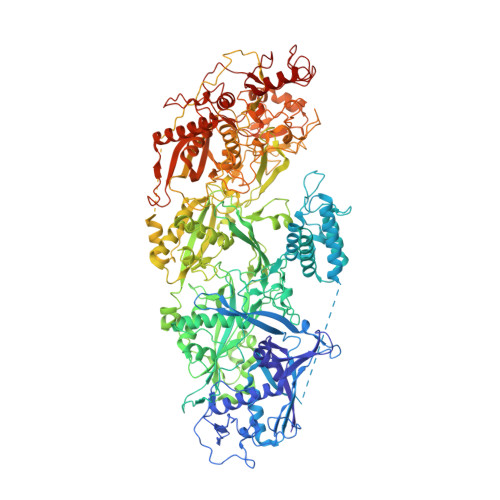
Craspase is a CRISPR RNA-guided, RNA-activated protease.
Hu, C., van Beljouw, S.P.B., Nam, K.H., Schuler, G., Ding, F., Cui, Y., Rodriguez-Molina, A., Haagsma, A.C., Valk, M., Pabst, M., Brouns, S.J.J., Ke, A.(2022) Science 377: 1278-1285
- PubMed: 36007061
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.add5064
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8D8N, 8D97, 8D9E, 8D9F, 8D9G, 8D9H, 8D9I - PubMed Abstract:
The CRISPR-Cas type III-E RNA-targeting effector complex gRAMP/Cas7-11 is associated with a caspase-like protein (TPR-CHAT/Csx29) to form Craspase (CRISPR-guided caspase). Here, we use cryo-electron microscopy snapshots of Craspase to explain its target RNA cleavage and protease activation mechanisms. Target-guide pairing extending into the 5' region of the guide RNA displaces a gating loop in gRAMP, which triggers an extensive conformational relay that allosterically aligns the protease catalytic dyad and opens an amino acid side-chain-binding pocket. We further define Csx30 as the endogenous protein substrate that is site-specifically proteolyzed by RNA-activated Craspase. This protease activity is switched off by target RNA cleavage by gRAMP and is not activated by RNA targets containing a matching protospacer flanking sequence. We thus conclude that Craspase is a target RNA-activated protease with self-regulatory capacity.
- Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: