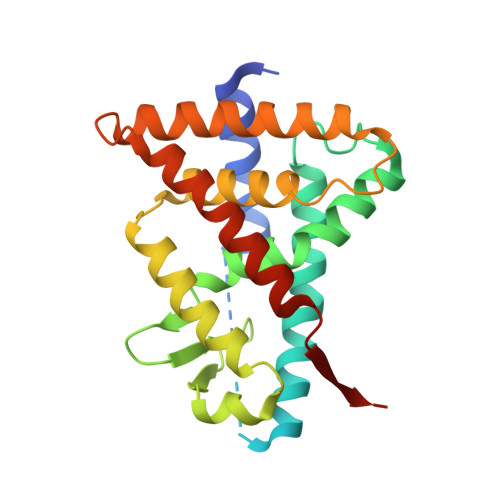
Structural basis of synthetic agonist activation of the nuclear receptor REV-ERB.
Murray, M.H., Valfort, A.C., Koelblen, T., Ronin, C., Ciesielski, F., Chatterjee, A., Veerakanellore, G.B., Elgendy, B., Walker, J.K., Hegazy, L., Burris, T.P.(2022) Nat Commun 13: 7131-7131
- PubMed: 36414641
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-34892-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8D8I - PubMed Abstract:
The nuclear receptor REV-ERB plays an important role in a range of physiological processes. REV-ERB behaves as a ligand-dependent transcriptional repressor and heme has been identified as a physiological agonist. Our current understanding of how ligands bind to and regulate transcriptional repression by REV-ERB is based on the structure of heme bound to REV-ERB. However, porphyrin (heme) analogues have been avoided as a source of synthetic agonists due to the wide range of heme binding proteins and potential pleotropic effects. How non-porphyrin synthetic agonists bind to and regulate REV-ERB has not yet been defined. Here, we characterize a high affinity synthetic REV-ERB agonist, STL1267, and describe its mechanism of binding to REV-ERB as well as the method by which it recruits transcriptional corepressor both of which are unique and distinct from that of heme-bound REV-ERB.
- Department of Pharmacology and Physiology, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, 63104, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: