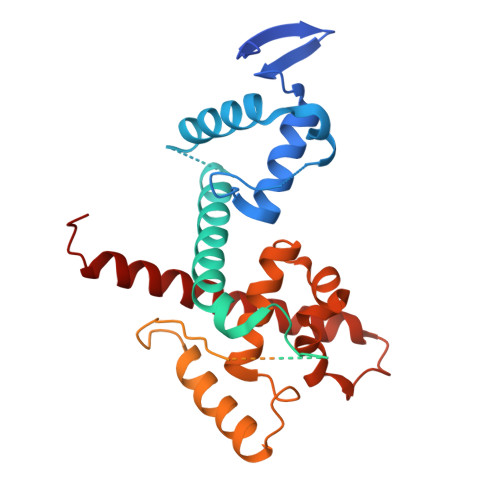
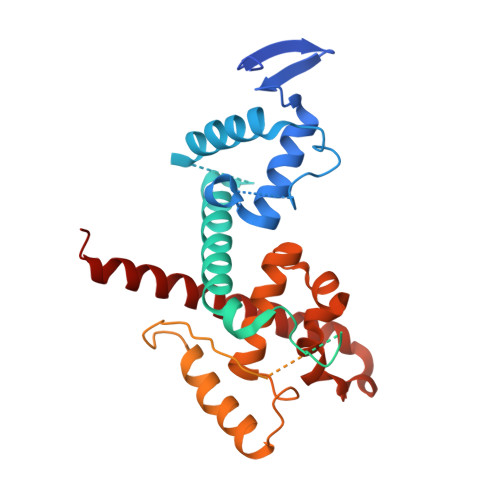
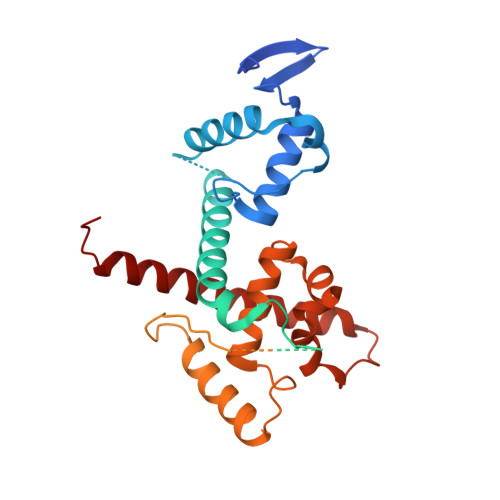
The role of auxiliary domains in modulating CHD4 activity suggests mechanistic commonality between enzyme families.
Zhong, Y., Moghaddas Sani, H., Paudel, B.P., Low, J.K.K., Silva, A.P.G., Mueller, S., Deshpande, C., Panjikar, S., Reid, X.J., Bedward, M.J., van Oijen, A.M., Mackay, J.P.(2022) Nat Commun 13: 7524-7524
- PubMed: 36473839
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-35002-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8D4Y - PubMed Abstract:
CHD4 is an essential, widely conserved ATP-dependent translocase that is also a broad tumour dependency. In common with other SF2-family chromatin remodelling enzymes, it alters chromatin accessibility by repositioning histone octamers. Besides the helicase and adjacent tandem chromodomains and PHD domains, CHD4 features 1000 residues of N- and C-terminal sequence with unknown structure and function. We demonstrate that these regions regulate CHD4 activity through different mechanisms. An N-terminal intrinsically disordered region (IDR) promotes remodelling integrity in a manner that depends on the composition but not sequence of the IDR. The C-terminal region harbours an auto-inhibitory region that contacts the helicase domain. Auto-inhibition is relieved by a previously unrecognized C-terminal SANT-SLIDE domain split by ~150 residues of disordered sequence, most likely by binding of this domain to substrate DNA. Our data shed light on CHD4 regulation and reveal strong mechanistic commonality between CHD family members, as well as with ISWI-family remodellers.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Life and Environmental Sciences, University of Sydney, The University of Sydney, NSW, 2006, Australia.