Crystal structure and induced stability of trimeric BxpB: implications for the assembly of BxpB-BclA complexes in the exosporium of Bacillus anthracis.
Chattopadhyay, D., Walker, D.R., Rich-New, S.T., Kearney, J.F., Turnbough Jr., C.L.(2023) mBio 14: e0117223-e0117223
- PubMed: 37382447
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.01172-23
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8D02 - PubMed Abstract:
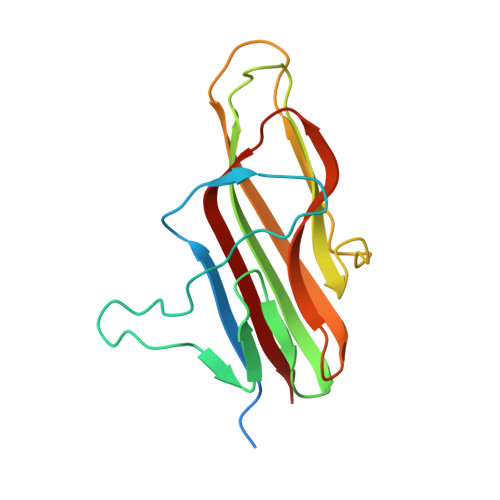
The outermost exosporium layer of Bacillus anthracis spores, the causative agents of anthrax, is comprised of a basal layer and an external hair-like nap. The nap includes filaments composed of trimers of the collagen-like glycoprotein BclA. Essentially all BclA trimers are attached to the spore in a process in which part of the 38-residue amino-terminal domain (NTD) of BclA forms an extremely stable interaction with the basal layer protein BxpB. Evidence indicates that the BclA-BxpB interaction is direct and requires trimeric BxpB. To further investigate the nature of the BclA-BxpB interaction, we determined the crystal structure of BxpB. The structure was trimeric with each monomer consisting of 11 β strands with connecting loops. The structure did not include apparently disordered amino acids 1-19, which contain the only two cysteine residues of the 167-residue BxpB. The orientation of the structure reveals regions of BxpB that could be involved in interacting with the BclA NTD and with adjacent cysteine-rich proteins in the basal layer. Furthermore, the BxpB structure closely resembles that of the 134-residue carboxyl-terminal domain of BclA, which forms trimers that are highly resistant to heat and detergent. We demonstrated that BxpB trimers do not share this resistance. However, when BxpB trimers are mixed with a peptide containing residues 20-38 of BclA, they form a complex that is as stable as BclA-BxpB complexes extracted from spores. Together, our results provide new insights into the mechanism of BclA-BxpB attachment and incorporation into the exosporium. IMPORTANCE The B. anthracis exosporium plays major roles in spore survival and infectivity, but the complex mechanism of its assembly is poorly understood. Key steps in this process are the stable attachment of collagen-like BclA filaments to the major basal layer structural protein BxpB and the insertion of BxpB into an underlying basal layer scaffold. The goal of this study is to further elucidate these interactions thereby advancing our understanding of exosporium assembly, a process shared by many spore-forming bacteria including important human pathogens.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medicine, University of Alabama at Birmingham , Birmingham, Alabama, USA.