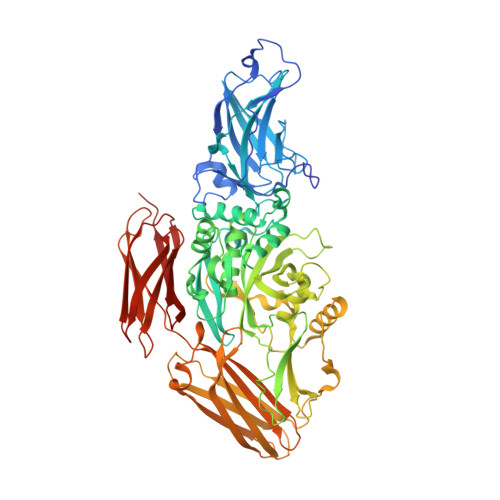
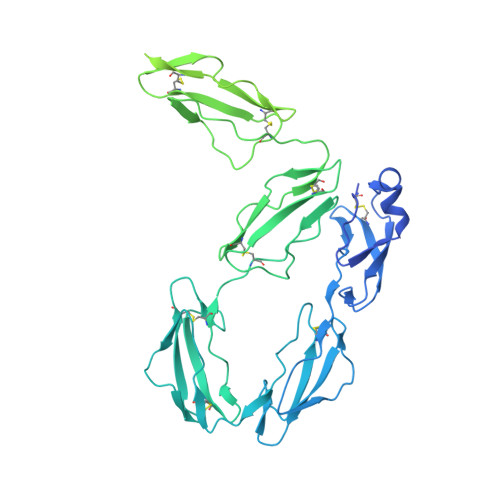
Cryo-EM structure of the human native plasma coagulation factor XIII complex.
Singh, S., Hagelueken, G., Ugurlar, D., Ramaraje Urs, S.U., Sharma, A., Mahapatra, M., Drepper, F., Imhof, D., Huesgen, P.F., Oldenburg, J., Geyer, M., Biswas, A.(2025) Blood 145: 438-449
- PubMed: 39447073
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2024025369
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8CMT, 8CMU - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of human coagulation factor XIII (FXIII), a heterotetrameric plasma pro-transglutaminase that covalently crosslinks pre-formed fibrin polymers, remains elusive until today. The heterotetrameric complex is composed of two catalytic FXIII-A and two protective FXIII-B subunits. Structural etiology underlying FXIII deficiency has so far been derived from crystallographic structures, all of which are currently available for the FXIII-A2 homodimer only. Here, we present the cryo-electron microscopy structure of a native, human plasma-derived FXIII-A2B2 complex at 2.4 Å resolution. The structure provides detailed information on FXIII subunit interacting interfaces as the two subunits interact strongly in plasma. The native FXIII-A2B2 complex reveals a pseudo-symmetric heterotetramer of two FXIII-B monomers intercalating with a symmetric FXIII-A2 dimer forming a "crown-like" assembly. The symmetry axes of the A2 and B2 homodimers are twisted relative to each other such that Sushi domain 1 interacts with the catalytic core of the A subunit and Sushi domain 2 with the symmetry related A' subunit and vice versa. We also report four novel mutations in the F13A1 gene encoding the FXIII-A subunit from a cohort of patients with severe FXIII deficiency. Our structure reveals the etiological basis of homozygous and heterozygous pathogenic mutations and explains the conditional dominant negative effects of heterozygous mutations. This atomistic description of complex interfaces is consistent with previous biochemical data and shows a congruence between the structural biochemistry of the FXIII complex and the clinical features of FXIII deficiency.
- Institute of Experimental Hematology and Transfusion Medicine, Bonn, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: