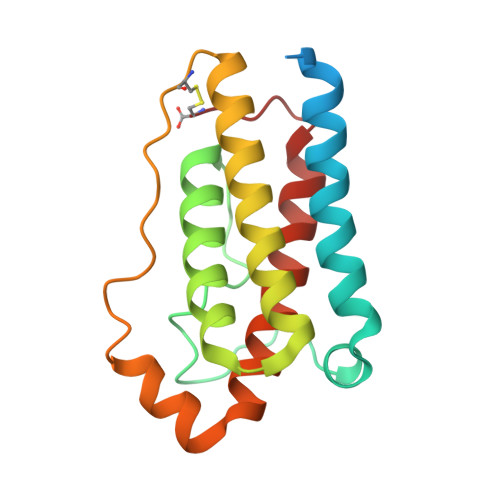
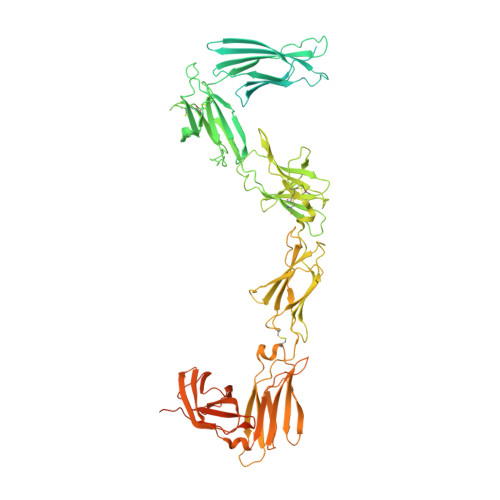Mechanism of receptor assembly via the pleiotropic adipokine Leptin.
Tsirigotaki, A., Dansercoer, A., Verschueren, K.H.G., Markovic, I., Pollmann, C., Hafer, M., Felix, J., Birck, C., Van Putte, W., Catteeuw, D., Tavernier, J., Fernando Bazan, J., Piehler, J., Savvides, S.N., Verstraete, K.(2023) Nat Struct Mol Biol 30: 551-563
- PubMed: 36959263
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-023-00941-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7Z3P, 7Z3Q, 7Z3R, 8AV2, 8AVB, 8AVC, 8AVD, 8AVE, 8AVF, 8AVO, 8B7Q - PubMed Abstract:
The adipokine Leptin activates its receptor LEP-R in the hypothalamus to regulate body weight and exerts additional pleiotropic functions in immunity, fertility and cancer. However, the structure and mechanism of Leptin-mediated LEP-R assemblies has remained unclear. Intriguingly, the signaling-competent isoform of LEP-R is only lowly abundant amid several inactive short LEP-R isoforms contributing to a mechanistic conundrum. Here we show by X-ray crystallography and cryo-EM that, in contrast to long-standing paradigms, Leptin induces type I cytokine receptor assemblies featuring 3:3 stoichiometry and demonstrate such Leptin-induced trimerization of LEP-R on living cells via single-molecule microscopy. In mediating these assemblies, Leptin undergoes drastic restructuring that activates its site III for binding to the Ig domain of an adjacent LEP-R. These interactions are abolished by mutations linked to obesity. Collectively, our study provides the structural and mechanistic framework for how evolutionarily conserved Leptin:LEP-R assemblies with 3:3 stoichiometry can engage distinct LEP-R isoforms to achieve signaling.
- Unit for Structural Biology, Department of Biochemistry and Microbiology, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium.
Organizational Affiliation: