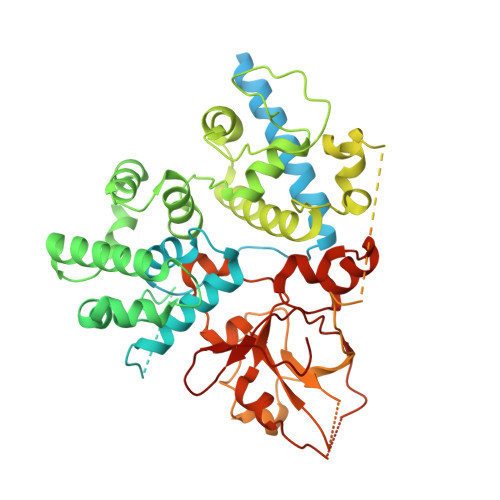
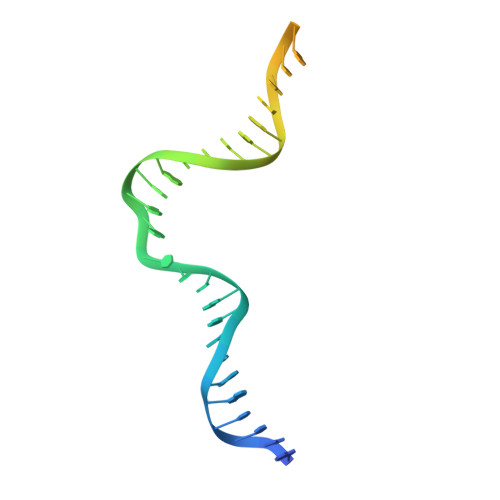
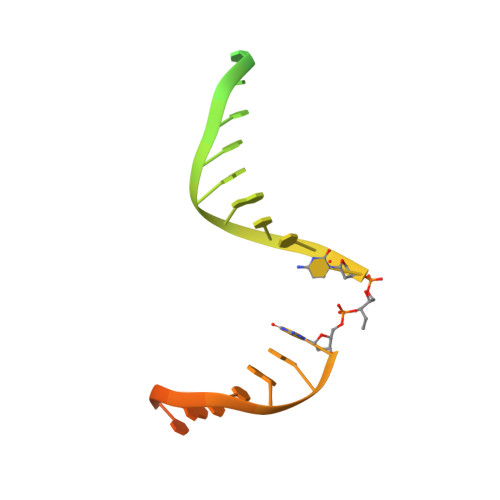
Molecular basis of the plant ROS1-mediated active DNA demethylation.
Du, X., Yang, Z., Xie, G., Wang, C., Zhang, L., Yan, K., Yang, M., Li, S., Zhu, J.K., Du, J.(2023) Nat Plants 9: 271-279
- PubMed: 36624257
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-022-01322-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7YHO, 7YHP, 7YHQ - PubMed Abstract:
Active DNA demethylation plays a crucial role in eukaryotic gene imprinting and antagonizing DNA methylation. The plant-specific REPRESSOR OF SILENCING 1/DEMETER (ROS1/DME) family of enzymes directly excise 5-methyl-cytosine (5mC), representing an efficient DNA demethylation pathway distinct from that of animals. Here, we report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of an Arabidopsis ROS1 catalytic fragment in complex with substrate DNA, mismatch DNA and reaction intermediate, respectively. The substrate 5mC is flipped-out from the DNA duplex and subsequently recognized by the ROS1 base-binding pocket through hydrophobic and hydrogen-bonding interactions towards the 5-methyl group and Watson-Crick edge respectively, while the different protonation states of the bases determine the substrate preference for 5mC over T:G mismatch. Together with the structure of the reaction intermediate complex, our structural and biochemical studies revealed the molecular basis for substrate specificity, as well as the reaction mechanism underlying 5mC demethylation by the ROS1/DME family of plant-specific DNA demethylases.
- Key Laboratory of Molecular Design for Plant Cell Factory of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Institute of Plant and Food Science, Department of Biology, School of Life Sciences, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China.
Organizational Affiliation: