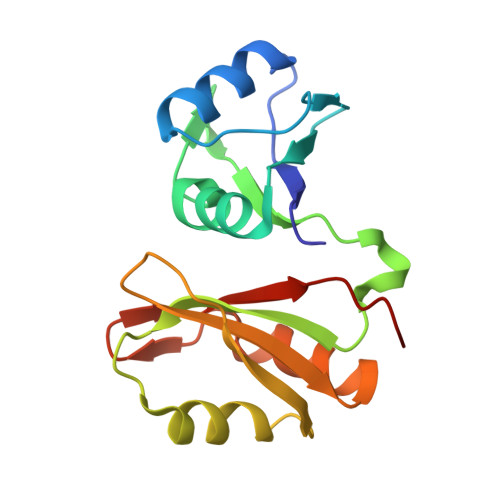
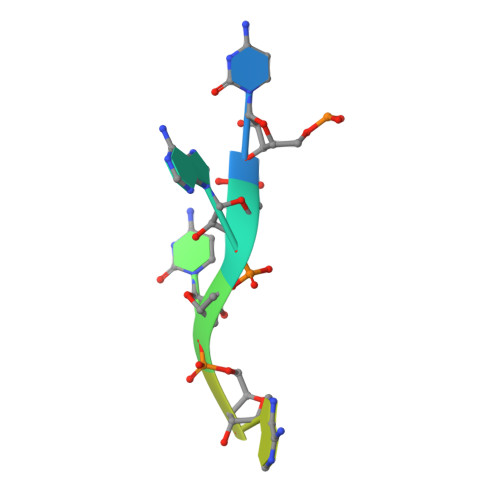
Structural basis for the RNA binding properties of mouse IGF2BP3.
Li, X., Guo, W., Wen, Y., Meng, C., Zhang, Q., Chen, H., Zhao, X., Wu, B.(2025) Structure
- PubMed: 39986276
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2025.01.022
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7VKL, 7VSJ, 7WW3, 7YEW, 7YEX, 7YEY - PubMed Abstract:
IGF2BP family proteins (IGF2BPs) contain six tandem RNA-binding domains (RBDs), resulting in highly complex RNA binding properties. Dissecting how IGF2BPs recognize their RNA targets is essential for understanding their regulatory roles in gene expression. Here, we have determined the crystal structures of mouse IGF2BP3 constructs complexed with different RNA substrates. Our structures reveal that the IGF2BP3-RRM12 domains can recognize CA-rich elements up to 5-nt in length, mainly through RRM1. We also captured the antiparallel RNA-binding mode of the IGF2BP3-KH12 domains, with five nucleotides bound by KH1 and two nucleotides bound by KH2. Furthermore, our structural and biochemical studies suggest that the IGF2BP3-KH12 domains could recognize the "zipcode" RNA element within the β-actin mRNA. Finally, we analyzed the similarities and differences of the RNA-binding properties between the KH12 and KH34. Our studies provide structural insights into RNA target recognition by mouse IGF2BP3.
- Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Malignant Tumor Epigenetics and Gene Regulation, Guangdong-Hong Kong Joint Laboratory for RNA Medicine, Medical Research Center, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510120, China; Department of Reproductive Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, China; Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou 510120, China.
Organizational Affiliation: