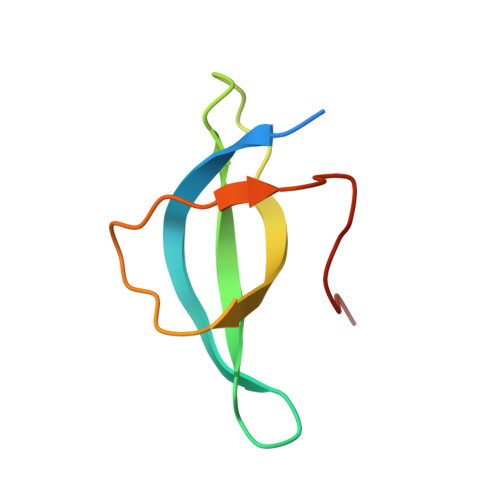
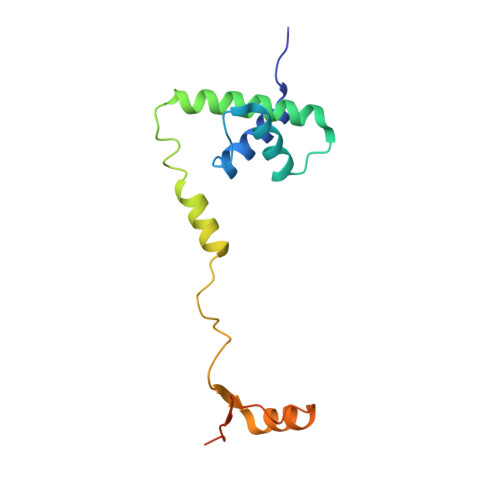
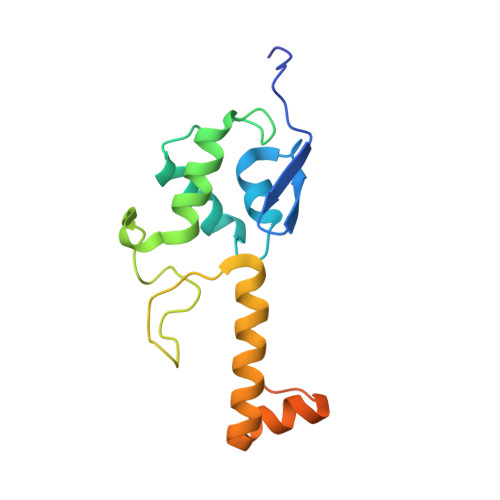
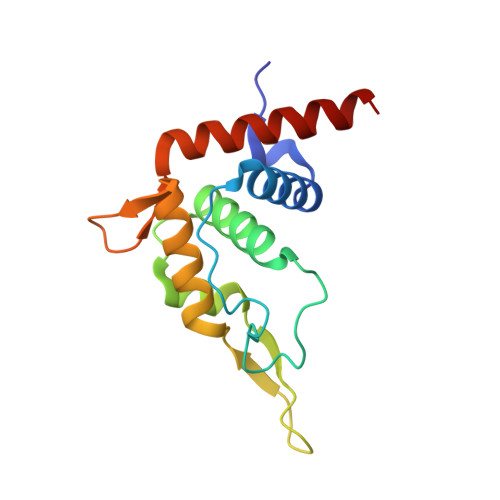
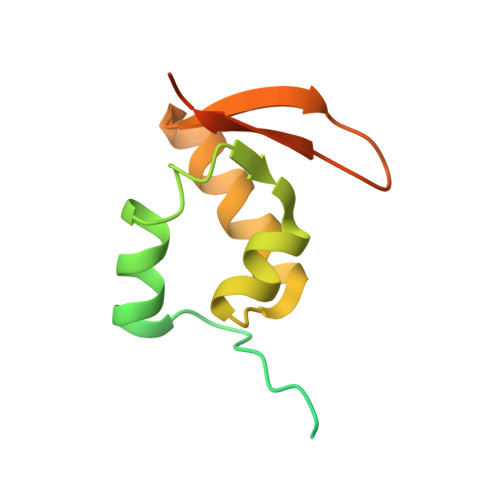
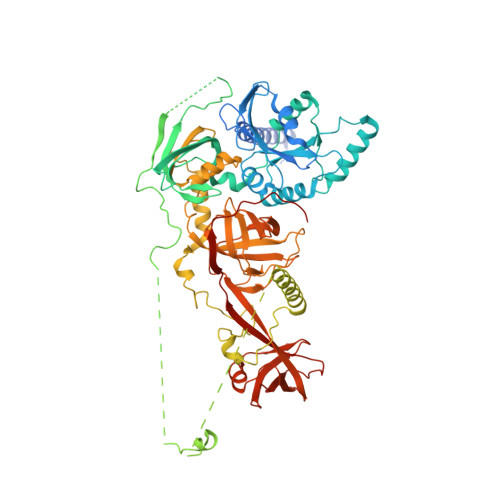
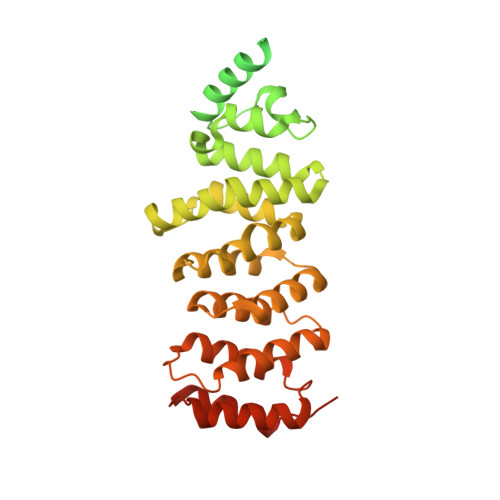
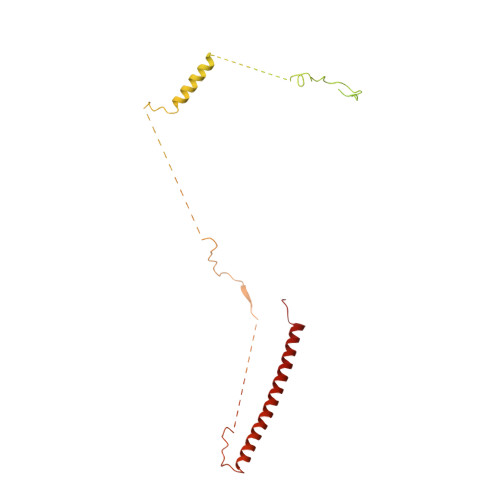
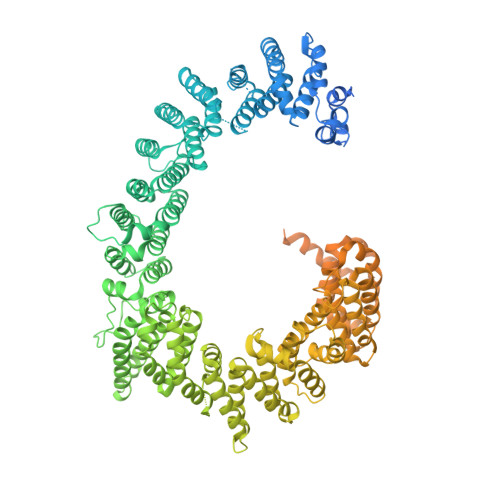
The nucleoplasmic phase of pre-40S formation prior to nuclear export.
Cheng, J., Lau, B., Thoms, M., Ameismeier, M., Berninghausen, O., Hurt, E., Beckmann, R.(2022) Nucleic Acids Res 50: 11924-11937
- PubMed: 36321656
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac961
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7WTN, 7WTO, 7WTP, 7WTQ, 7WTR, 7WTS, 7WTT, 7WTU, 7WTV, 7WTW, 7WTX, 7WTZ, 7WU0 - PubMed Abstract:
Biogenesis of the small ribosomal subunit in eukaryotes starts in the nucleolus with the formation of a 90S precursor and ends in the cytoplasm. Here, we elucidate the enigmatic structural transitions of assembly intermediates from human and yeast cells during the nucleoplasmic maturation phase. After dissociation of all 90S factors, the 40S body adopts a close-to-mature conformation, whereas the 3' major domain, later forming the 40S head, remains entirely immature. A first coordination is facilitated by the assembly factors TSR1 and BUD23-TRMT112, followed by re-positioning of RRP12 that is already recruited early to the 90S for further head rearrangements. Eventually, the uS2 cluster, CK1 (Hrr25 in yeast) and the export factor SLX9 associate with the pre-40S to provide export competence. These exemplary findings reveal the evolutionary conserved mechanism of how yeast and humans assemble the 40S ribosomal subunit, but reveal also a few minor differences.
- Gene Center and Department of Biochemistry, University of Munich LMU, Feodor-Lynen-Str. 25, 81377 Munich, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: